About Us
Executive Editor:Publishing house "Academy of Natural History"
Editorial Board:
Asgarov S. (Azerbaijan), Alakbarov M. (Azerbaijan), Aliev Z. (Azerbaijan), Babayev N. (Uzbekistan), Chiladze G. (Georgia), Datskovsky I. (Israel), Garbuz I. (Moldova), Gleizer S. (Germany), Ershina A. (Kazakhstan), Kobzev D. (Switzerland), Kohl O. (Germany), Ktshanyan M. (Armenia), Lande D. (Ukraine), Ledvanov M. (Russia), Makats V. (Ukraine), Miletic L. (Serbia), Moskovkin V. (Ukraine), Murzagaliyeva A. (Kazakhstan), Novikov A. (Ukraine), Rahimov R. (Uzbekistan), Romanchuk A. (Ukraine), Shamshiev B. (Kyrgyzstan), Usheva M. (Bulgaria), Vasileva M. (Bulgar).
Geological-mineralogical sciences
An earlier study of structural and textural characteristics of the pathogenic aggregates showed that their formation occurs by stages. In the process of stone formation, the composition of physiological solutions is undergoing significant, often periodic, multi-phase change is manifested in the rocks, their microheterogeneity zoning and variable composition of most pathogenic biominerals. It has been found that the stones, mineral components consisting of organic compounds (oxalate and urinary uric acid, cholesterol holelits), usually have a spherulitic structure and direct the growth phase of supersaturated solutions. Phosphate stones (phosphate uroliths, dentolits and salivolits) are characterized by a grainy texture and formation of cryptocrystalline material deposition (sedimentation). In mixed, both the mechanism of formation of stones can occur. Since the greatest amount of mixed stones uroliths, they have a layered structure in which grain Cryptocrystalline spherulite formation and metabolism.Methods of modeling allow to reveal features of processes of emergence of new growths in a human body and action of the systems regulating their growth. At the same time studying of formation of a number of minerals in not to peculiar environment for them with accurately regulated conditions of a human body different (sometimes very significantly) from conditions of the abiogenous environment, expands idea of genesis of minerals and promotes development of the general theory of mineralogenesis.
Methods of thermodynamic modeling received broad distribution in geochemical researches for the description of processes of mineralogenesis with participation of mainly diluted solutions. The solution of a task includes use of the corresponding criterion answering to a condition of stable equilibrium of system, and thermodynamic a reasonable choice of association of minerals which can potentially be in balance with environment for this limited area of conditions. Change of standard energy of Gibbs at formation of a deposit is connected with work of solubility of slightly soluble connection by the equation:
![]() (1) where –
(1) where – ![]() Gibbs's standard energy, kJ/mol; R – universal gas constant (J / моль∙К); T – temperature, K.
Gibbs's standard energy, kJ/mol; R – universal gas constant (J / моль∙К); T – temperature, K.
One of ways of graphic representation of balance the sediment ↔ rastvor in system in which formation of almost insoluble connection from water solution proceeds, is construction of "stability fields" (fig1). The principle of creation of similar charts consists in establishment of functional dependence of the minimum concentration of the cation which is a part of a deposit which needs to be created for receiving supersaturation on this phase, from рН solution and concentration of anion: 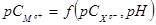
During the carried-out thermodynamic calculations conditions and possibility of formation of almost insoluble connections in hypothetical solution of sediment-forming ions are revealed. On the basis of the constructed charts of stability for a series of phosphates of calcium and magnesium, and also calcium oxalate, areas at which formation of these phases from solutions most thermodynamic is probable are defined.
Thermodynamic calculation reflects possibility of formation of phases only proceeding from data on their thermodynamic stability in a standard condition and doesn't consider, in particular, the kinetic factors having impact on process of formation of a solid phase in actual practice.
When carrying out model experiments analogs of phosphatic minerals were received, and also distinctions in the conditions of their education are revealed. The analysis of the obtained data showed that size рН solution has the most essential impact on structure of a being formed solid phase. Thus the variation of initial concentration of components of solution, in the range of values, characteristic for biological liquid, brings in the basic to quantitative, instead of to high-quality changes of structure of a deposit.
On the basis of thermodynamic and experimental simulation in prototypes of biological fluids we identified physico-chemical parameters of the formation of poorly soluble compounds that make up the urinary tract, salivary and dental calculus in the body. It has been shown that the most stable phase of pathogenic minerals is apatite, the formation of which is possible in a wide range of pH and concentrations of stone forming components. This result explains well the most common pathogens in the apatite units in the human body. In the formation of calcium oxalate, which is dominated by minerals of kidney stones, a crucial role is played by kinetic factors.
The results obtained indicate relevance and prospectively of the research into crystallization of pathogenic phases in human organism on model systems in order to identify the mechanisms that control their genesis.
Acknowledgements. This work was partially supported by the Russian Fund for Fundamental Research (grant № 15-29-04839 ofi_m, № 15-33-50250 mol_nr).
Golovanova O.A. THERMODYNAMIC AND EXPERIMENTAL SIMULATION OF CRYSTALLIZATION PROCESSES IN PROTOTYPES OF BIOLOGICAL FLUIDS. International Journal Of Applied And Fundamental Research. – 2015. – № 2 –
URL: www.science-sd.com/461-24863 (19.04.2024).











 PDF
PDF