About Us
Executive Editor:Publishing house "Academy of Natural History"
Editorial Board:
Asgarov S. (Azerbaijan), Alakbarov M. (Azerbaijan), Aliev Z. (Azerbaijan), Babayev N. (Uzbekistan), Chiladze G. (Georgia), Datskovsky I. (Israel), Garbuz I. (Moldova), Gleizer S. (Germany), Ershina A. (Kazakhstan), Kobzev D. (Switzerland), Kohl O. (Germany), Ktshanyan M. (Armenia), Lande D. (Ukraine), Ledvanov M. (Russia), Makats V. (Ukraine), Miletic L. (Serbia), Moskovkin V. (Ukraine), Murzagaliyeva A. (Kazakhstan), Novikov A. (Ukraine), Rahimov R. (Uzbekistan), Romanchuk A. (Ukraine), Shamshiev B. (Kyrgyzstan), Usheva M. (Bulgaria), Vasileva M. (Bulgar).
Materials of the conference "EDUCATION AND SCIENCE WITHOUT BORDERS"
Now a day key role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) indifferent physiological and pathological processes is clearly defined [3-5]. At other side, most mechanisms of exogenous ROS action are described in details. In addition, a result of interstitial generation of these substances is not so clear [1, 3, 5]. It is supposed, that one of its action ways is enzymes activity regulation [2]. That is why the aim of this work is estimation of ROS effects on catalytic activity of some blood enzymes.
Material and methods. We studied 25 specimens of whole human blood. Each experiment included separation of specimen in 4 portions, first of its is control (without any manipulations). Second portion was treated by gaseous oxygen, third one was bubbled with ozone-oxygen mixture (ozone concentration – 3000 mcg/l) and fourth portion was oxygenated (as second one) with subsequent processing by darsonvalization during 5 min. Exposition time after exposure was 3 min.
In blood plasma of these specimens after processing we studied the activity of lactate dehydrogenase, hydroxybutirate dehydrogenase, creatine kinase and its MB-fraction with automatic biochemical analyzer «Clima MC-15» (Spane) with original reagents.
Statistic processing of the data was accomplished by the programs Microsoft Excel 2003 and Primer of Biostatistics 4.03. The descriptive statistics data is shown in the article.
Results. It is stated, that lactate dehydrogenase activity was elevated under all used exposures, but level of this increasing is variable significally (fig. 1). Particularly, simple oxygenation and its combination with darsonvalization leads to maximal stimulation of this enzyme activity (at 1.21 and 1.22 times to control level respectively; p<0.05). Blood ozonation adduces to minimal changes of this parameter (at 1.072 times to control).
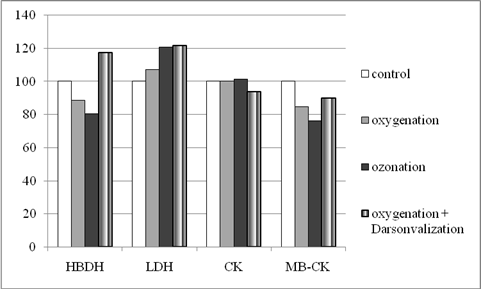
Fig. 1. Blood enzymes activity under different reactive oxygen species processing (LDH - lactate dehydrogenase, HBDH - hydroxybutirate dehydrogenase, CK - creatine kinase, MB-CK - MB-fraction of creatine kinase)
Activity of hydroxybutirate dehydrogenase is known as isoform-1 of lactate dehydrogenase was gently decreased under oxygenation and ozonation of blood samples (on 11.3% and 19.7% to control, respectively; p<0.05). On the contrary, activity of this enzyme elevated under complex exposure (at 1.18 times; p<0.05).
Total creatine kinase activity of blood plasma was most stable to all investigated exposures, excluding combination of oxygenation and darsonvalization. In this case we fixed moderate reduction of indicated enzyme activity.
At other side, activity of MB-fraction of creatine kinase was decreased equally for all estimated exogenous factors. Maximal reduction of this parameter was registered for blood ozonation (at 23.8% to control level; p<0.05). Smaller enzyme fraction inhibition was observed in simple oxygenation and its combination with darsonvalization.
Conclusion. So, blood processing with reactive oxygen species reduces to changes of different plasma enzymes activity, but most optimal dynamics of its catalytic properties was registered for intra-blood (as model of liquid biological tissue) generation of ROS. It includes activation of lactate dehydrogenase and hydroxybutirate dehydrogenase with minimal inhibition of creatine kinase and its MB-fraction.
2. Peretyagin S.P., Martusevich A.K., Solovyeva A.G. et al. Enzymological evaluation of hepatotropic effect of ozone in a subchronic experiment // Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine. 2013. Vol. 154, Iss. 6. P. 789-791.
3. Peretyagin S.P., Martusevich A.K., Struchkov A.A. et al. Respiratory Function and Blood Gases Transport State at Experimental Hypoxia: Ozone Therapy Correction // Revista Espanola de Ozonoterapia. 2012. Vol. 2, №1. P. 141-146.
4. Rosen G.M., Tsai P., Pou S. Mechanism of free-radical generation by nitric oxide synthase // Chem. Rev. 2002. Vol. 102. P. 1191-1199.
5. Stanley W.C., Recchia F.A., Lopaschuk G.D. Myocardial substrate metabolism in normal and failng heart // Physiol. Rev. 2005. Vol. 85. P. 1093-1129.
Martusevich A.K., Soloveva A.G., Ivannikova E.V. Action of reactive oxygen species on catalytic activity of some blood enzymes in vitro. International Journal Of Applied And Fundamental Research. – 2013. – № 2 –
URL: www.science-sd.com/455-24179 (28.02.2026).











 PDF
PDF