About Us
Executive Editor:Publishing house "Academy of Natural History"
Editorial Board:
Asgarov S. (Azerbaijan), Alakbarov M. (Azerbaijan), Aliev Z. (Azerbaijan), Babayev N. (Uzbekistan), Chiladze G. (Georgia), Datskovsky I. (Israel), Garbuz I. (Moldova), Gleizer S. (Germany), Ershina A. (Kazakhstan), Kobzev D. (Switzerland), Kohl O. (Germany), Ktshanyan M. (Armenia), Lande D. (Ukraine), Ledvanov M. (Russia), Makats V. (Ukraine), Miletic L. (Serbia), Moskovkin V. (Ukraine), Murzagaliyeva A. (Kazakhstan), Novikov A. (Ukraine), Rahimov R. (Uzbekistan), Romanchuk A. (Ukraine), Shamshiev B. (Kyrgyzstan), Usheva M. (Bulgaria), Vasileva M. (Bulgar).
Materials of the conference "EDUCATION AND SCIENCE WITHOUT BORDERS"
In this work given a justification of the method of fictitious domains. For the first time obtained not improving mark of convergence rate of the solving the from auxiliary problem to solving the original problem at the time when the small parameter strive to zero.
The fictitious domain method is one of the known methods of approximate solutions of boundary value problems in mathematical physics. In general fictitious domain method is justified for the linear boundary value problems of mathematical physics. In this work is devoted to substantiation of the fictitious domain method for nonlinear elliptic equations. A new method of obtaining best possible rate of convergence of solutions in the method of fictitious domains .
Let's consider the boundary value problem for nonlinear elliptic equations in
![]() area with border area
area with border area
![]()
![]() , (1)
, (1)
![]() . (2)
. (2)
As method of fictitious domains for the continuation of the lower coefficient in the auxiliary area
![]() with border
with border
![]() Ø, solving equation with small parameter
Ø, solving equation with small parameter
![]() , (3)
, (3)
![]() , (4)
, (4)
where
![]() - continued with zero out of
- continued with zero out of
![]() and
and
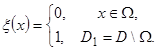
Next one notations used are from the monograph
Definition 2.1.1. Generalized solution of the exercises (3), (4) is the function
![]() , that is
satisfying the integral identity
, that is
satisfying the integral identity
![]() (5)
(5)
for all
![]() .
.
Theorem 1. Let’s
![]() .
Then there exists a unique weak solution
(3)-(4) and it is satisfied the estimate
.
Then there exists a unique weak solution
(3)-(4) and it is satisfied the estimate
![]() (6)
(6)
where
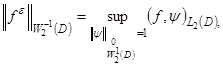
at that, when
![]() this solution converges to the generalized solution of the problem
(1), (2).
this solution converges to the generalized solution of the problem
(1), (2).
Definition 2. Stronger solution of the problem (3)-(4) is called function
![]() , that satisfying to equation (3) almost everywhere.
, that satisfying to equation (3) almost everywhere.
Theorem 2.1.2. Let’s
![]()
![]() . Then there a stronger solution of the problem (3)-(4) and it is satisfied the estimate
. Then there a stronger solution of the problem (3)-(4) and it is satisfied the estimate
![]()
![]() , where
, where
![]() at
at
![]() . (7)
. (7)
Theorem 2. Let’s
![]()
![]()
![]() . Then
. Then
![]() (8)
(8)
![]() - positive constant that not depend from
- positive constant that not depend from
![]() .
.
2. Смагулов Ш.С. Метод фиктивных областей для краевой задачи уравнений Навье-Стокса .- Новосибирск, 1979,(Предпринт/ВЦ СО АН СССР, №68.-С. 68-73.
3. Коновалов А.Н. Численные методы механики сплошной среды.-1972.-Т.3,№5. –С. 52-67.
Kuttykozhayeva Shakharzat Nurtaevna, Bekteleuova Akbota Algabasovna MATHEMATICAL MODELLING OF THE TASKS OF HYDRODYNAMICS
BY THE METHOD OF FICTITIOUS AREAS
. International Journal Of Applied And Fundamental Research. – 2013. – № 2 –
URL: www.science-sd.com/455-24310 (24.02.2026).











 PDF
PDF