About Us
Executive Editor:Publishing house "Academy of Natural History"
Editorial Board:
Asgarov S. (Azerbaijan), Alakbarov M. (Azerbaijan), Aliev Z. (Azerbaijan), Babayev N. (Uzbekistan), Chiladze G. (Georgia), Datskovsky I. (Israel), Garbuz I. (Moldova), Gleizer S. (Germany), Ershina A. (Kazakhstan), Kobzev D. (Switzerland), Kohl O. (Germany), Ktshanyan M. (Armenia), Lande D. (Ukraine), Ledvanov M. (Russia), Makats V. (Ukraine), Miletic L. (Serbia), Moskovkin V. (Ukraine), Murzagaliyeva A. (Kazakhstan), Novikov A. (Ukraine), Rahimov R. (Uzbekistan), Romanchuk A. (Ukraine), Shamshiev B. (Kyrgyzstan), Usheva M. (Bulgaria), Vasileva M. (Bulgar).
Philological sciences
Introduction
Attempting to perceive the surrounding life`s real existence, the human recognizes the following qualities and descriptions as a beauty and ugliness, fact or false of real image which are appeared on his mind. The simple conceptual cognitive is realized by renewed creative activities through drawing instruments which refer to symbols, sounds and art.
The kinds of art have a good influence to foundation of emotional relations for life`s reality and beauty in the art by affecting to human`s mind through the images which made by private artistic-expressive instruments. In the art, variety of fine art`s nature, its meaning and content, a grand quantity of making methods, its role in the foundation of spiritual-material world outlook and aesthetic relation of human to surrounding life`s real existence are shown in the philosophic, aesthetic, art historic works of the following scientists like A.Burov, U.Borev, V.Bachinin, A.Zis, B.Baizhigitov, B.Kazykhanova.
But, according to the learning problems of fine art in our country, the difficulties referring to developing process of drawing, ability, skillfulness, the upbringing importance of art were considered as the main problems. They are problems about the influence of psychological factors referring to art history which play a major role in teaching to fine art are out from research. Art teaching is a long, difficult practical, pedagogical and psychological process. The concept of psychology is the research problem of influence of psychic process to artistic actions, ability and creative quality in the art. The comprehensive, learning, recognizing process of art, and reasoning in the aesthetic style level are directly connected with perceiving quality.
Perception is the fundamental process of subjective image which is appeared due to the results of direct influence of the environment things, phenomenon and processes to the feeling organs (seeing, hearing, tasting and smelling).
In the process of teaching of school children and students of Pedagogical universities to fine art, the following methods of pedagogic specialists should be the main duty of art learning and aesthetic educational activities: discussion of drawing methods and art creations, teaching of research capability in accordance with the creative knowledge requirement (practical actions), development of basic knowledge about the art`s importance in the spiritual-aesthetic education (pedagogical process), realizing of fine art by means of the closely relation of psychical factors like perception, feeling, influence, cognitive, conclusion in the art history content.
Research objective: During the preparing of future fine art teacher, it’ s necessary to show the easy using importance of psychical process`s phenomenon in the content of teaching of school teachers and children to fine art in spite of the age difference. To enhance the knowledge about psychological factors which enable to study the art and the content of pedagogical-methodic studying activities of students in practical drawing.
The main chapter. The pedagogical science examines the fine art as the creative knowledge and aesthetic education tool which enables the person to face with spiritual cultural values. Art psychology is the science which researches the psychical regularities of emotional affection referring to the viewer of the creative art makers` actions. The researchers of art psychology [6, 7, 10, 11] pay more attention to perceptive process which arise the creative activities to the qualitative level and its psychical qualities like feeling, thinking, cognition. Aesthetic feeling is a wide concept. Firstly, it is the capability of truthful appreciation of human`s perception of environment views.
Surrounding real existence is an inexhaustible source of feeling and sense, but the sense is a subjective image of truth which is appeared on human`s mind. Developing person`s aesthetic feeling, and expanding his concept about beauty and style, it helps to be formed and developed in the future.
The correct understanding of this system enables to define the different features of perception during the studying of fine art, therefore, it also helps to find the solution of the concept about subjective of art image of life`s reality in the art.
The scientific findings which are associated with psychological formation, tools, regularities and educational importance referring to art perception of art in the factors which influence on person`s spiritual-aesthetic formation were defined in psychological works of the following scientists: L.S.Vygotskii, M.M.Mukhanov, S.L.Rubinshtein, V.K.Skatershikov, B.M.Teplov, P.M.Yakobson, B.P.Yusov. Psychologist L.S.Vygotskii made the conclusion about the perception`s importance of art by saying: «Any theory of art is based on the view that is established in the study of perception, in the study of the feeling, imagination and fantasy» [6, 240]. Also, psychologist B.M.Teplov claimed this conclusion by saying: «The perception of art has to begin with feeling... without it, it is impossible, but the art perception isn't limited by feeling. At first, this perception is "feeling", and then "thinking", besides very deeply and penetrating». [9, 10]. Thus, the psychologists consider that the perception is very important problem which is examined in the closely relation with different components of psychical process that are associated with human`s cognitive actions. Also, they consider it as a source of knowledge which leads to relation in accordance with artist`s surrounding truth and beauty regularities as the indivisible structural elements of art activities in the art.
In the process of sense, when the artist perceives the objects, phenomenon, things that have to be drawn, the image of this reality is come on his mind and sensual, emotional impression is appeared for them. The sense in the time of looking and perceiving the object, cognition and thinking are considered as indivisible psychic process during the drawing of real image, but their quality and result of art activities can be in the different level. In a one case, the perception has superiority through controlling that based on the objective according to the human`s general development and mood, in another case, the outcome of impressive feeling which is appeared from the depth of perception influences to develop the cognitive activity that provides the creative actions to be qualitative [2, 25-26].
Cognition is not only shining view of truthful existence in human`s brain, it is also difficult function of intellectual movement that directs from ignorance to knowledge, from raw concept to full concept. It is well known from psychology that the cognition of high level leads to people`s mind conclusion, figurative and material reasoning. The top level of cognitive process is reasonable thinking, making a conclusion, being able to argue. The art cognition in the art is realized due to outcome of direct relation between artist and environment. In this way, first of all, the action of artist takes its beginning from researching the life`s real existence through feeling, its description and qualitative features of personal particles. Also, it takes its foundation from making the conclusion about the regularities between their relation and connection. The artist carries out the following operations during the perception and feeling of thing or phenomenon through cognition, which contribute on making the conclusion like comparison, discussion, synthesizes, abstraction, generalization, specification of objects on his mind. It separates an artist from subjective wrong conclusion about real existence. Making the conclusion enable an artist to define and to recognize the criterions of art description and the meaning of object from these features and relations, also it gives him an opportunity to control the events and phenomenon, to predict his results of drawing actions. Moreover, a one of the main objective of fine art`s teaching process at school is to give a chance for children to enhance their art thinking and to get the new level.
The abilities to estimate, to feel, to argue, to feel of beauty are begining formed at the child.
The student's drawings which are trained in the fine arts show the separate characteristic of object of drawing, its interaction with environment, activity level. The author of article who gives an assessment to quality of drawing was convinced of it in long pedagogical to practice. Proceeding from pedagogical experience, future teacher of graphic art, the student shows that he has an important practical knowledge for development of emotional feelings which are necessary for formation of graphic knowledge. Due to this problem when the performing tasks on drawing of objects and subjects of the fine arts for check of level of emotional influence on their thinking, level of perception of students the special practice is carried out. 13 students of two courses during certain time were given three various natyurmortny statements 3 look depending on a task after 2-3 weeks works were presented:the first is a jug from clay, apple and poletenets; the second is a jug from clay, apple, the white material lying on a table; the third is an effigy, apple, the rosella lying a little across, the material lying on a table [2, 27].
After the students attentively surveyed still life, it was offered to them to describe in writing each still life in compliance with below the provided demands:
1. To describe the still life exhibitions on the discretion (without accurate restrictions, full freedom is given at the description)
2. To write features of subjects of still life (sequence of a statement isn't specified)
3. Having attentively studied still life subjects, to describe keeping ways of phasing in compliance to classes in drawing.
The written description of values and analysis of quality of the graphic works are taken from practice showed the following results: the first at the free description isn't present cleaning of systemic uniformity, the form, color, material, the invoice of a subject was consistently described. Secondly, when performing a task according to the demand there was a certain sharpness, there was no monotony at analysis of difficult subjects and figures which have different structure. At the beginning students began analysis with the biggest subject - a clay jug, then about 65%-the plaster rosella, 30%-a clay jug, 5%-began with the apple which is in the foreground closer to the audience. In answers of the third task most of students supplied with the information similar to the description of the second task. It was noticed that the students participating on a practical task still didn't master methodical ways of the image of still lifes consisting of the plane with a set of subjects according to the law of the fine arts.
The researches devoted to studying of laws of the fine arts show the arising problems because of not the qualitative taken measures when performing practical tasks, the works of students of pedagogical educational institutions influencing to quality:
1) the disadvantages which are arising because of superficial perception of objects, the represented subjects;
2) because of superficial perception, because of depression of emotional and cognitive activity, disadvantages the image of object in consciousness of the artist;
3) the nature of object, a mistake resulting from the wrong comprehension of features;
4) the practical mistakes which are arising in the course of an illustration of a volume subject on the plane [2, 27] .
The group of these shortcomings follows one another helps to generate other. For example, shortcomings of perceptions affect the distortion of personal image of painted things, these two shortcomings leads to an incorrect understanding of the artistic and expressive paintings. From this, set goals and responsibilities for the implementation of tasks in the area of methodological requirement to teach students to perceive the action, using it to develop students' aesthetic sense, knowledge of the visual arts, rightly thinking about art and all it has to take the title place in the pedagogical practices of the teacher.
In the initial stages of mastering the fine arts teacher should find out and explain to the causes of shortcomings in the work of his pupil, and teach him the ways to address these shortcomings is the main duties lecturer. And the duty is one of the main problem in the school of artificial knowledge and educational trends. Psychology of age especially, the children's attitude to the phenomenon and things divided into two different ratings are pleasant and unpleasant. Interest in elegance is a special desire of a child to the knowledge of something or a certain phenomenon. The child is interested to know about decorated, bright, iridescent things. Feelings of interest are attraction to the perception of the needs of the child and phenomenon that carried out the emotional satisfaction of a work of art, works of art and other action. Development at the level of the knowability of the qualities of interest and imitation under the influence of specially organized educational work develops a child's desire to be creative. Paying attention to the interest in the creativity and the properties of the experience of the child, and the development outlook, imagination, knowledge, creative perception should take the title place in the the innovative methods of teaching the student. In aesthetics, art criticism talks about the importance of emotional satisfaction than the feeling that you get from art classes. Because a work of art doesn’t only affect the person's thinking but also his inner world. Based on this without knowing the feeling that you get from the Arts we have not a desire to know and to be engaged with the art. This phenomenon and needs are closely associated with aesthetic style that defines the capability of differentiating the beauty, glory, misunderstanding, confrontation from spiritual cultural values, art creations, image of surrounding life`s reality. Aesthetic style includes the truth of life in all appropriate relations. The authors of special works associated with taste (Zh.Aymauytov, Yu.Borev, M.Mukanov, B.Nemensky, V.Skaterschikov, B.Yusov) believe that aesthetic style and creativity are the main component of aesthetic education and are based on the rich possibilities arts to determine means and the principal factors that influence the development of personality. V.K.Skaterschikov in his work "About the aesthetic styles" examines the aesthetic work of humans and the environment as a power that controls the aesthetic perception, and says so"creative style is an ability to define the beauty of homeliness, the sheer beauty of the artificial" [8, 34]. Zh.Aymauytov in his book "The system of the soul and a selection of art," thinks so: "A human with the birth inclined to a certain art, each person has a desire and ability" it reveals the meaning of the skill formation of style [1, 123]. If you concider these findings as training in the fine arts is "Creative taste" is the direct influence of art is determined by the level will develop a quality mastering skills art society and the individual and based on the unity of the different mental processes that arise from the perception of the relevant requirements of works of art, as well as the driving force level of ability rises to the desired level of quality of aesthetic education. The main object of considering the art style nature as the capability is the qualitative result of creative activities and cognition in the making of art image which are done by artist (poet, writer, compositor, painter, art master) in order to show the real existence`s phenomenon. Thus, during the process of realizing the duties of art knowledge and aesthetic education, keeping the turn of two style concepts that fills each other is considered as important pedagogical requirement.
The system module of art teaching is made by the teaching new requirements of fine art and definition of methodical directions of realizing. The education program and the content of «System of training in the fine arts at school» [2, 34-46] book which prepared by the author of article is made in accordance with that module and it is using in the educational process.
Systematic module covers the following main directions based on taking the control by teacher in order to define the duties and objective of art knowledge and spiritual-aesthetic education, to form by uniting the requirements of teaching technology of subject`s content with psychological process. (look at the tabular):
1. To educate the developing means of esthetic education and art knowledge to the school pupils by subject’s content (The types of art; the genres of art; an expressive language of art).
2. The forms of art and aesthetic foundation of pupils through fine art subject, exactly, the art activities and subjective communication in the fine art lesson and the kinds of art and aesthetical activities apart from lesson have been emphasized.
3. The connection of teaching the art with psychological process (perception – emotional feeling impression – figurative imagination – spatial thinking - art understanding - esthetic style – to discuss understanding and thinking and etc.).
4. The pedagogical process of formation of the pupils’ esthetic education by art: diligence is being an interest of the pupils in art and their interest of relation in making beauty, in receiving art knowledge; pithiness is planning of teaching the subject in accordance with educational possibilities and function of art; Tendency is defining the formative directions of art knowledge, art skills and abilities which realize the pupils` aesthetic education.
5. It the content of the subject «fine art», by developing the creative skills and capabilities of pupils, it is possible to notice that the content of art-aesthetic formation is a system of practical art works; the problems of psychological formation; to give the aesthetic education through teaching the spiritual, cultural values [2, 123-124].
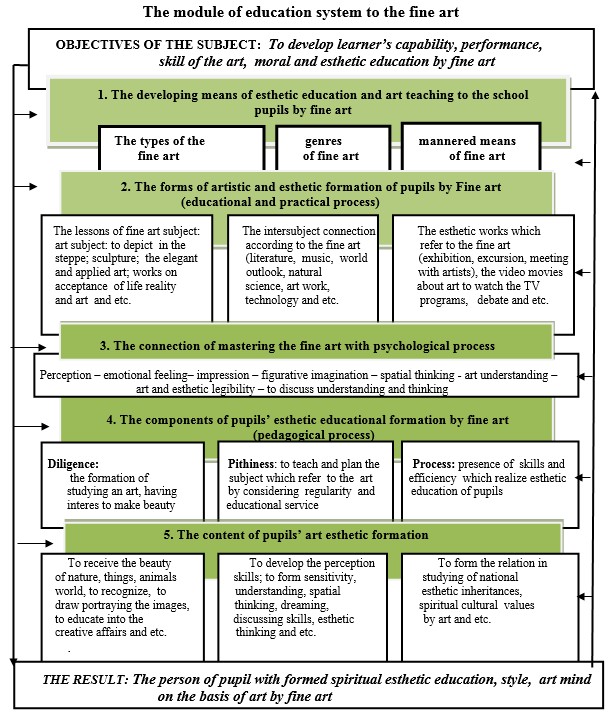
Deduction. A number of quantities of art instruments, genres and types of the fine arts are a method of education of spiritual culture which gives the opportunity for person to receive the art knowledge, by means of favorable usage of social, esthetic, educational functions of various practical art activities and arts, during its stage of studying. But this pedagogical process is not only realized by drawing actions.
We can not achieve a good result without doing work on shaping the development of the practical work of art, the development of the individual works of art in an enclosed truthfulness, feelings, experience, formation of mental phenomena as cognition. Based on this we can say that the primary responsibility of every teacher is to prepare future teachers of the art in universities, schools, the system of students’ training, proper objectivity of student’s perception of art skill, sensitivity, creativity, in addition to the development of the knowability also need to take into account such items as planning, organization. [2, 32-33]. Сreation of pictorial images in the visual arts and the perception of a work of art, research, development analysis, the importance of maintaining the interaction of practical, pedagogical and psychological knowledge is born in the peculiarities inherent in the art.
Conclusion. At the initial stage of development of the arts, the primary responsibility of training in this area is truth of life, the laws of the limited art education cognitive and aesthetic attitudes to things and natural phenomena, teacher education and creative research is inherent in professional content, showing the direction. Training of future teachers of fine art works should be achieved by giving artistic knowledge, maintaining a consistent system of education:
1) The process of learning the fine arts: to organize three ways are closely interconnected. This is primarily psychological- perception of matter and the phenomenon must be mentioned in the order, feeling the impact of sensation and cognition, the second is practice which allows to develop students' skills of fine art, ability, creative vision, and the third is pedagogic allowing to solve the methodological issues in school as a tutor of the future, giving artistic knowledge and aesthetic education of young calcined using the fine arts;
2) Full usage of the methods and sources of psychological knowledge allows to examine, to analyze, to feel, to feel the physical, visual description and features described things and objects with the aim of perception during the students’ work on the fine arts.
3) Formation of assessment skills and disassembly of qualities between each stage of the work of students in the fine arts and to its full closure in accordance with the laws of art, with the purpose and responsibility of the task.
If these problems of studying and education, on the one hand are pedagogical requirements of preparing of future school teachers as a professional, on the other hand these problems are the defining factor of levels of the psychological relation of teachers and students to literature.
2. Kamak A. System of training of a subject of the fine arts at school. Textbook (Sistema obuchenya izobrazitelnomu iskusstvu v shkole. Uchebnik. Na kaz.iazyke / Almaty: Orchon, 2014. - 288 p. (in Kazakhstan)
3. Мukanov М. Sphere of intelligence (Sfera intellekta /Akyl-oi orysy. Na kaz.iazyke). - Аlmaty: Kazakhstan, 1990. (in Kazakhstan)
4. Borev Yu. Esthetics /Эстетика. – М., 1988. - 496 p. (in Russian).
5. Vygotsky L. Art psychology (Psychologya iskusstva – М.,1987. - 240 p. (in Russian).
6. Меilach Б. Art perception as scientific problem. In book: Art perception (Chudozhestvennoe vospriatie kak nauchnaia problema. V knige: Chudozhestvennoe vospriatie). – L., 1971.
7. Skaterschikov V. Скатерщиков В.К. About the aesthetic styles (Ob esteticheskom vkuse). – М.: Znanie, 1974. - 95 p. (in Russian).
8. Teplov B. Abilities and endowments. Chosen works. Volume 1 (Sposobnosti i odarennosti. Izbrannye trudy. Tom 1). – М.,1987. (in Russian).
9. Yakobson P. Psychology art perception (Psichologia chudozhestvennogo vospriatia). - М., 1988.
10.Yusov B. Perception of art and age features of school students. In book: A role of the art museums in esthetic education of school students. P.1. Vospriatie iskusstva I vozrastnye osobennosti Shkolnikov. V kn.: Rol chudozhestvennykh museev v esteticheskom vospitanyi shkolnikov. Ch. 1. – М., 1973. (in Russian).
Kamak Abdikarim PSYCHOLOGICAL FACTORS OF LEARNING THE FINE ARTS AT SCHOOL. International Journal Of Applied And Fundamental Research. – 2014. – № 2 –
URL: www.science-sd.com/457-24684 (14.03.2026).











 PDF
PDF