About Us
Executive Editor:Publishing house "Academy of Natural History"
Editorial Board:
Asgarov S. (Azerbaijan), Alakbarov M. (Azerbaijan), Aliev Z. (Azerbaijan), Babayev N. (Uzbekistan), Chiladze G. (Georgia), Datskovsky I. (Israel), Garbuz I. (Moldova), Gleizer S. (Germany), Ershina A. (Kazakhstan), Kobzev D. (Switzerland), Kohl O. (Germany), Ktshanyan M. (Armenia), Lande D. (Ukraine), Ledvanov M. (Russia), Makats V. (Ukraine), Miletic L. (Serbia), Moskovkin V. (Ukraine), Murzagaliyeva A. (Kazakhstan), Novikov A. (Ukraine), Rahimov R. (Uzbekistan), Romanchuk A. (Ukraine), Shamshiev B. (Kyrgyzstan), Usheva M. (Bulgaria), Vasileva M. (Bulgar).
Teaching science
Ensuring of competitiveness of graduates of higher school, technical secondary school, certainly, is urgent problem both in theoretical, and practical plan. Its decision is directly linked to increase of quality of training of students and especially with rational distribution of academic hours onto learning by students of didactic units of subjects.
Scientific novelty of the research consists in offered approach to forming of variable part and the programs of disciplines (of base cycle) of Educational Standards on basis of method of sum of places at use of structural averages and of offered coefficient of profile value of concrete thematic block of the subject.
It is necessary to note, that considering of Bologna process implication of representatives of potential employers to external estimation of activity of higher educational institutions is momentous from positions both theoretical, and practical training of graduates. Specified matter of fact possibly and importantly to take into account at distribution of academic hours of this or variant forming educational subject and of its the program among didactic units on base of structural averages estimations of experts.
Practical importance of the research consists in possibility of more valid and rational distribution of academic hours of formed subject onto didactic units on base of structural average estimations of experts, including potential employers of graduates and, supervention, in increase of quality of training of the latter and their competitiveness.
In offered approach median (version of structural average) represents quantitative estimation, countable in marks, of opinions of experts (groups of experts) describing importance of this or other didactic unit of subject for concrete competence from all ones, related to interesting subject according to Educational Standard.
In the approach use of interval series and calculation for those of structural average is represented rather expedient, when opinions of experts from adjacent, but differing areas of professional activity are found out.
Application of median is especially topical, when totality of experts (groups of experts), opinions is patchy. As to the mode, its use in context of the soluble problem is represented of having sense, when smaller, but sharply standing out part of interrogated experts is unanimous in estimations and necessity of modification into this or that educational program already has ripened in society.
Let's we have indicator of event A, consisting in crossing of the interesting i-th thematic block (didactic unit) of forming subject with j-th special subject of graduating department.
Let's then indicator of event B, consisting in crossing of interesting i-th thematic block of formed subject with q-th graduating department.
Let's also
indicator of event T, consisting in
crossing of interesting i-th
thematic block of forming subject with n-th
theme of graduation qualification paper (GQP) of q-th graduating department, and at each crossing each of
indicators ![]() ,
,
![]() ,
, ![]() accepts value 1, else accordingly accepts value 0.
accepts value 1, else accordingly accepts value 0.
Taking into account accepted designations, coefficient of profile value of i-th thematic block (didactic unit) of subject for graduate of appropriate profile will develop into
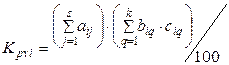 ,
,
where ![]() is the total amount of subjects of GQP of the q-th graduating department, with which the
i-th thematic block of the
subject is crossed,
is the total amount of subjects of GQP of the q-th graduating department, with which the
i-th thematic block of the
subject is crossed,
s, k, p is accordingly amount of special subjects, of graduating departments of institution, of themes of GQP of the q-th graduating department (at crossing for appropriate case of the i-th thematic block of the subject).
According to
method of sum of places, which, as a rule, is used at estimation of financial
status of enterprises, we are ranked the didactic units; as shown, e. g., in
tab. 1. Symbol "![]() "
in the leftmost column in designation of coefficient
"
in the leftmost column in designation of coefficient ![]() means ranking on decrease (the higher values the better).
means ranking on decrease (the higher values the better).
Tab. 1.
Median (mode) of estimations of experts (up to 100 marks), ![]() and its ranking
and its ranking
|
Characteristics |
Didactic units of subject (sections) |
|||||
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
||||
|
Competence N01 |
72 |
1 |
50 |
3 |
59 |
2 |
|
Competence N02 |
75 |
2 |
45 |
3 |
79 |
1 |
|
|
1,76 |
2 |
2,08 |
1 |
1,68 |
3 |
|
|
- |
5 |
- |
7 |
- |
6 |
Thus, after ranking on decrease (for all competences and in view of the coefficient), as it is visible from results of summation of appropriate right positions of tab. 1, the section 2 of the subject is the most important among three presupposed sections for graduate, and then in decreasing order the sections: 1 and 3.
More detail the approach is stated in paper [1].
Sheptunov M. V. ON APPROACH TO FORMING OF SUBJECTS OF VARIABLE PART OF EDUCATIONAL STANDARDS ON BASE OF METHOD OF SUM OF PLACES AT USE OF STRUCTURAL AVERAGES. International Journal Of Applied And Fundamental Research. – 2014. – № 3 –
URL: www.science-sd.com/458-24594 (03.03.2026).











 PDF
PDF