About Us
Executive Editor:Publishing house "Academy of Natural History"
Editorial Board:
Asgarov S. (Azerbaijan), Alakbarov M. (Azerbaijan), Aliev Z. (Azerbaijan), Babayev N. (Uzbekistan), Chiladze G. (Georgia), Datskovsky I. (Israel), Garbuz I. (Moldova), Gleizer S. (Germany), Ershina A. (Kazakhstan), Kobzev D. (Switzerland), Kohl O. (Germany), Ktshanyan M. (Armenia), Lande D. (Ukraine), Ledvanov M. (Russia), Makats V. (Ukraine), Miletic L. (Serbia), Moskovkin V. (Ukraine), Murzagaliyeva A. (Kazakhstan), Novikov A. (Ukraine), Rahimov R. (Uzbekistan), Romanchuk A. (Ukraine), Shamshiev B. (Kyrgyzstan), Usheva M. (Bulgaria), Vasileva M. (Bulgar).
Chemical sciences
Introduction
The development of modern technology requires the development of new and perfection of existing methods of obtaining nanosized biocompatible materials with high performance. Such materials include oxide spinel on the basis of ferrite of zinc. Scientific interest in studying processes of phase formation and properties of such materials due to, primarily, their multifunctional properties. It is known that zinc ferrite is an n-type semiconductor [1], is considered as the electrode material [2], acetone sensor [3]. One of the promising areas of application of biocompatible ferrites is the possibility of their use for targeted drug delivery. Typically, the synthesis of materials with the spinel structure occurs at elevated temperatures, for a long time or requires the of special equipment. In this connection development of methods of synthesis, the study of the processes of formation of phases and properties of materials in the system ZnO-Fe2O3 is of fundamental and practical interest for modern material science. The aim of the study was to study the processes of structure formation of nanosized zinc ferrite using different techniques.
Materials and methods study
For the synthesis of zinc ferrite ZnFe2O4 composition of the used methods, described in detail in [4, 5]. As starting substances were used in solutions of Nitrates of zinc and iron (III) with a concentration of 1 mol/l aqueous solution of ammonia NH3•H2O concentration 25% (mass.), citric acid C6H8O7 concentration of 6.25 mol/l, and polyacrylamide. The initial substance in accordance with the formulation was placed in a steel reaction vessel and was heated to complete decomposition of the organic component. Phase composition was studied by x-ray diffractometer ARL X'TRA (used Cu-Kα radiation), the definition of surface area were performed with the use ChemiSorb 2750 in the CCU In "Nanotechnology" Institute of Nanotechnologies and new materials SRSPU(NPI).
Results and discussion
The samples were obtained with two methods. 1. Mixed salt solutions with ammonia solution and added polyacrylamide (sample 1). 2. Mixed salt solutions with ammonia solution and citric acid added (sample 2). The solutions were evaporated and subjected to heat treatment to complete degradation of organic matter. On radiographs of the samples (Fig. 1) contains only lines describing the phase cubic spinel structure of ZnFe2O4 (PGF Number 010-74-2397).
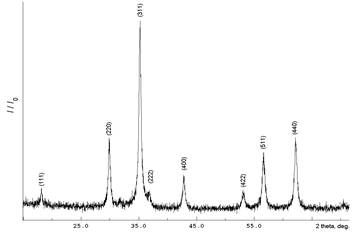
Fig. 1. The roentgenogram of the sample ZnFe2O4.
The resulting material has the form of a loose porous powder with a developed surface. In Fig. 2 shows a micrograph of the sample. The values of the surface area of the synthesized material, measured by BET, was as follows: for sample 1 SBET = 248 m2/g for sample 2 SBET =453 m2/g.

Fig. 2. Micrograph of sample ZnFe2O4.
The obtained results can be useful for selecting magnetic materials with a developed surface, are promising for applications as transducers , sensors, catalysts, etc.
Conclusions
Studied the process of formation of spinel structure of composition ZnFe2O4 . The results can be used to develop easily separable materials with a developed surface, such as sensors, adsorbents, catalysts.
2. Thankachan, R.M. Enhanced lithium storage in ZnFe2O4-C nanocomposite produced by a low-energy ball milling / R.M. Thankachan, M.M. Rahman, I. Sultana et al. // Journal of Power Sources. 2015. V. 282. P. 462-470.
3. Zhang, Ji. ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization, and enhanced gassensing property for acetone / Ji. Zhang, Ji-M. Song, H.-L. Niu et al. // Sensors and Actuators. 2015. V. B 221. P. 55–62.
4. Shabelskaya, N.P. The study of the processes of structure formation of ferrite-chromites of transition elements / N.P. Shabelskaya, A.I. Vlasenko, S.I. Sulima, E.V. Sulima // International Journal of Applied and Fundamental Research. 2015. No. 8. P. 99-103.
5. Shabelskaya N.P. Phase Formation Processes in the NiO – CuO – Fe2O3 – Cr2O3 System upon Salt Decomposition // Inorganic Materials. 2014. V. 50. No. 11. P. 1114-1118.
Shabelskaya N.P., Vlasenko A.I. SYNTHESIS OF NANOSIZED ZINC FERRITE. International Journal Of Applied And Fundamental Research. – 2015. – № 2 –
URL: www.science-sd.com/461-24857 (28.02.2026).











 PDF
PDF