About Us
Executive Editor:Publishing house "Academy of Natural History"
Editorial Board:
Asgarov S. (Azerbaijan), Alakbarov M. (Azerbaijan), Aliev Z. (Azerbaijan), Babayev N. (Uzbekistan), Chiladze G. (Georgia), Datskovsky I. (Israel), Garbuz I. (Moldova), Gleizer S. (Germany), Ershina A. (Kazakhstan), Kobzev D. (Switzerland), Kohl O. (Germany), Ktshanyan M. (Armenia), Lande D. (Ukraine), Ledvanov M. (Russia), Makats V. (Ukraine), Miletic L. (Serbia), Moskovkin V. (Ukraine), Murzagaliyeva A. (Kazakhstan), Novikov A. (Ukraine), Rahimov R. (Uzbekistan), Romanchuk A. (Ukraine), Shamshiev B. (Kyrgyzstan), Usheva M. (Bulgaria), Vasileva M. (Bulgar).
Chemical sciences
Nowadays in pharmaceutics nano-porous carbon materials are in wide use that is explained, by sum total of their original properties including high indicators of specific surface and porosity, chemical stability in aggressive mediums and also great possibilities in variety of their properties by selection of initial raw material, and conditions for its processing. In last decade of great interest is obtaining and studying the properties of functional materials on the base of nano-structutal systems with given physico-chemical properties.
Carbon nano-structural materials (CNM) are related to the more perspective modern materials for therapeutic purposes, a wide sphere of use of those is caused by originality of their physico-mechanical and adsorptional properties and also developed porous structure. CNM can be applied as adsorbents and matrix for immobilization with further targeted delivery of medicinal substance to the necessary organ. In this case therapeutic nano-technology provides the transport of medicinal substance to the focus of pathological process and allows getting the increase of effectiveness of the very existing medicinal therapy. Delivery of medicines with the help of porous nano-particles will allow also increasing considerably the degree of their medical action. Appearance of new adsorbents and increasing the amount of existing ones will allow solving this problem basing on versatility of properties of CNM-adsorbents and their advantages in the number of parameters over classical adsorbents. In this regard, elaboration of new carbon materials types with nano-porous structure, working out the technology of their production and studying their adsorptional and desorptional descriptions is a very current problem.
The aim of this research is studying nano-structural adsorptional material on the base of nano-porous activated charcoal and determination its physico-chemical descriptions and sorptional properties. One of the branches in creation of versatile highly-effective adsorbents is modification of classical adsorbents – activated charcoal, ceolites, silicagels by carbon nano-structural material with the purpose of increasing the surface area and their effectiveness. Purposeful obtaining and regulation of structures and properties of carbon carriers is carried out in the process of their obtaining on the account of different reaction ability of carbon components of carrier related to oxygen-containing activated agents and also selecting the ratio of carbon components in the carrier and properties of technical carbon. Further step in development of sorptional therapy methods is connected with the use of selective adsorbents. The first step on the way of creation selective materials is regulation of sorptional materials’ pores size [Cartel N.Т. and others, 1995], i.e. adsorbents’ pores must be compared with size of extracted molecules.
Summarized surface and volumetric descriptions of carbon adsorbent AC-C obtained on the base of analysis of adsorption isotherms are presented in Table 4.3.
Table 4.3.
Surface and volumetric descriptions of AC-C adsorbents on nitrogen
|
Adsorbent |
Sвет, m2/g |
V∑ , сm3/g |
Vmi, cm3/g |
W, cm3/g 1,6nm<r<157,4 nm |
|
Carbonizate |
370 |
0,36 |
0,15 |
0,21 |
|
AC-C with activation degree of 50% |
635 |
0,73 |
0,257 |
0,399 |
|
AC-C with activation degree of 70% |
1050 |
0,92 |
0,46 |
0,63 |
Porometric descriptions of AC-C with activation degree of 50% on adsorption of nitrogen are presented in the table. It is interesting to note that the evaluation of pores size can be made both on adsorptional branch of isotherm and on desorptional one. Calculation on desorption data provides the radius of pore’s neck and on adsorption data-radius of its spare place.
Table 4.4.
Results of porometric analysis of AC-C on nitrogen adsorption
|
Adsorbent |
Rср micropores, nm |
R of pores, nm |
Semi-width of micropores, nm |
Adsorption energy, kJ/mole |
Smi, m2/g |
|
|
adsorption |
desorption |
|||||
|
АC-C |
1,257 |
1,533 |
1,933 |
0,6709 |
19,376 |
712,181 |
From the obtained results (Table. 4.4.) can be made conclusion that the radius of the most narrow pore’s part limiting the velocity of desorption process proceeding is 1,933 nm, and adsorption– 1,533 nm, that plays important role in studying kinetics of adsorption-desorption processes, particularly, taking into account the size of toxic substances’ molecules.
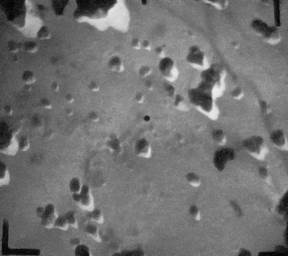
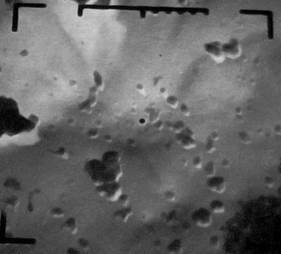
So, in Fig. 4.12 are presented photos of AC-C with burn degree of 70% with increasing up to 1: 20000, which allow to observe macropores with diameters of 100-350nm.
|
а) |
б) |
Fig.4.12. Electron-microscopic photos of АC-C (scale 20000:1) with particles size
from 100 nm to 500 nm (а) and from 100 nm to 700 nm (b).
Ismailova M.G., Abzalova N.A., Abzalov A.A. DETERMINATION OF PHYSICO-CHEMICAL DESCRIPTIONS AND SORPTIONAL PROPERTIES OF CARBON NANO-STRUCTURAL MATERIALS. International Journal Of Applied And Fundamental Research. – 2015. – № 2 –
URL: www.science-sd.com/461-24880 (28.02.2026).











 PDF
PDF