About Us
Executive Editor:Publishing house "Academy of Natural History"
Editorial Board:
Asgarov S. (Azerbaijan), Alakbarov M. (Azerbaijan), Aliev Z. (Azerbaijan), Babayev N. (Uzbekistan), Chiladze G. (Georgia), Datskovsky I. (Israel), Garbuz I. (Moldova), Gleizer S. (Germany), Ershina A. (Kazakhstan), Kobzev D. (Switzerland), Kohl O. (Germany), Ktshanyan M. (Armenia), Lande D. (Ukraine), Ledvanov M. (Russia), Makats V. (Ukraine), Miletic L. (Serbia), Moskovkin V. (Ukraine), Murzagaliyeva A. (Kazakhstan), Novikov A. (Ukraine), Rahimov R. (Uzbekistan), Romanchuk A. (Ukraine), Shamshiev B. (Kyrgyzstan), Usheva M. (Bulgaria), Vasileva M. (Bulgar).
Medical sciences
Introduction
Multiple myeloma (MM) - B-cell lymphoproliferative disease, major morphological substrate which are clonal plasma cells producing monoclonal immunoglobulin Ig A, IgG, IgD, IgE and light (k,l) chains
It is well known that MM is quite common in all countries disease, found at people of all races, average age of male patients is at 68 years, for women -70 years, it is considered as "a disease of older age". The incidence of this disease is about 1%. The lowest incidence of multiple myeloma in the Republic of China by frequency is 1(one) case per 100 000 population per year.
According to the author [4] observes, that in recent years in Russia there is a tendency to rejuvenation of the disease, patients occur more frequently likely in middle-aged populations of 3-4 cases per 100 000 population per year.
The authors in [3] describes that the disease is often detected in the later stages, there are no criteria in changes the blood, which are markers of malignancy especially in the early stages of its development.
Implementation of allogeneic bone marrow transplantation is currently carried out mainly patients who have HLA-identical siblings. The number of such patients is not more than 30-35%, which is a bone marrow transplantation, in this connection, efforts for using such categories donors such as relatives of the recipient is not fully coincident with HLA-antigens and unrelated donors, matched entirely in the HLA- phenotype. The most promising is unrelated donors, fully matched by HLA-phenotype.
At the same time, we know, that not for all ethnic peoples and nationalities can be found compatible donor, to this end immuno-selective methods extremely important detection donors at systems antigens HLA-alleles I and II of class, at which identity the bone marrow the donor and the patient, testifies to their full compatibility.
The author in work[5] written that for every ethnic of the people and nationalities needs its own "control sample" which is dictated by both population-specific character of HLA among a healthy population, thus and the possibility of interpopulation differences in HLA-markers with genetic predisposition to one or another disease
In recent years, among the ethnic peoples is difficult to find a compatible donor hematopoietic stem cells in the European and American registers that which necessitated creation of its own register of bone marrow donors, on an example China, Japan [1].
And at the present stage for the conversion of bone marrow transplantation in the treatment method and study genetic HLA diversity of the inhabitants of different regions of the country, need national registers, which will be closely in cooperation search donors as well as the expansion of the data base on potential donors of hematopoietic stem cells with the identification of histocompatibility antigens I and II class
However, due poorly studied largely frequency of antigens of HLA, among different ethnic peoples and nationality to date it causes fundamental difficulties.
The authors of [2], conducted of study immunogenetic and populations characteristics in the distribution of antigens HLA alleles in the system HLA I and II class patients with multiple myeloma kirghiz nationality.
To compare these results, patients with multiple myeloma kirghiz nationality, we have conducted its own research of the major complex histocompatibility antigens in potential donors kirghiz nationality.
The aim of our study is to investigate the immunological and genetic characteristics in the distribution on system alleles HLA-I and II class at patients with multiple myeloma and donors hematopoietic stem cell the kirghiz nationality.
Materials and methods:
To study the immunological and population characteristics of the system HLA-alleles of I class loci (A and B), were typed of 127 voluntary donors kirghiz ethnicity nationality(54 women and 73 men) from the National Register of hematopoietic stem cells of Kirghizia from1998 to 2009
To study the immunological and population characteristics of the system HLA-alleles of I class loci (A and B), were typed of 127 voluntary donors kirghiz ethnicity nationality(54 women and 73 men) from the National Register of hematopoietic stem cells of Kirghizia from1998 to 2009 years, of which 78 donors (16 women and 62 men) the typed of II class DRB1* locus in age from 18 to 50 years. The studies were conducted in the laboratory immunohaematology Russian Research Institute of Hematology and Transfusiology.
The data were compared with a control group of patients with multiple myeloma -22 kirghiz ethnic nationality observed at the National Hospital in the Ministry of Health of the citizens of the Kirghiz Republic, typing of system-HLA alleles 1 and II classes from October 1995 to March 1999 in the laboratory of immunology St. Petersburg Clinical hospital number 31 (the Clinical Center of advanced medical technologies)[1].
Avia- transportation and delivery analysis was conducted in patients with MM in mini refrigerated containers at -10 ° C.
TYPING OF HLA-ANTIGENS I CLASS:
Determination of HLA- loci (A and B) phenotypes of surveyed persons was carried out serological method using a panel of sera gistotipiruyuschih antileykotsitarnyh Russian Research Institute of Hematology and Transfusiology, allowing to define the locus of antigens 17 "A" and 27 "B" the locus of antigens.
TYPING OF HLA-ANTIGENS II CLASS:
Molecular typing of HLA- genes a locus DRB1* was performed by the polymerase chain
reaction using a set of primers domestic firm "DNА-technology"(Moscow) allows to select 13 groups of alleles HLA-DRB*1 (basic resolution). Genomic DNA was isolated of peripheral blood mononuclear cell (fresh or frozen at -20°C), stabilized with sodium citrate or EDTA(final concentration 0.5% of anticoagulant), by using a set reagents "NPF DNA technology"(Moscow),or using immunomagnetic method recruiting firm «Dynal»All stages of amplification were conducted on a thermocycler "TERTSIR"DNA technology ", Moscow).The product obtained in the amplification determined by the method horizontal electrophoresis in 3.2% of agrarian gel with visualization under ultraviolet light L= 320 nm.The specificity of the amplification product were compared with standard marker of DNA lengths PUC-09.
THE RESEARCH OF IMMUNOGLOBULINS:
Achieved the by direct immunoassay, paraproteins were immobilized on a solid phase of sera diluted 1:105 and 1:106 in 0:1 M carbonate-bicarbonate buffer pH-9,5.Izotipy types of heavy chains and light chains of myeloma immunoglobulins conjugates were determined in using monoclonal antibodies (СMA) horseradish peroxidase.
Statistical processing of the results obtained included the analysis of standard criteria. X2-square
was used to estimation of reliability differences in the detection certain limitations between control group and the patients MM. Determination of the value "p", corresponding value found. X2-square was carried out considering of one degree of freedom.
All mathematical calculations and statistical analysis of the overall study was performed using a personal computer using the package application programs for spreadsheets -"Microsoft - Excel M version 7.0, for Windows 95, for Windows-based 2010, Statistica-5.
Results and discussion:
Our studies among a small kirghiz nation, in the system HLA 1 -II class revealed, that by the frequency of occurrence there are the most common and very distinguishing series of genes.
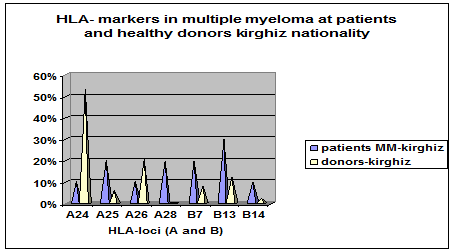
Figure 1. Immunogeneticheskie markers in patients with multiple myeloma and of healthy donors bone marrow of kirghiz nationality.
At comparative the characteristics in results analysis of the system HLA- alleley class 1 loci (A and B) multiple myeloma patients and healthy donors kirghiz nationality, the data are presented in Figure 1, reveals, that significant and important immunogenetic markers characteristic for patients with multiple myeloma kirghiz ethnic nation and found genes HLA-A24 in 10% of cases, HLA-A25 in 20%, HLA-A26 in 10%, HLA-A28 in 20%, HLA-B7 in 20%, HLA-B13 in 30.0% and HLA-B14 in10% of cases.
And most common by frequency of occurrence among in healthy donors of HLA-A24 genes in 53,1%, HLA-A26 to 20,4%, HLA-B7 at 8,2%, HLA-B13 in 12,2% and somewhat less HLA gene -A25 about 6,1% of cases, practically encountered in rare cases the gene HLA-B14 about 2, 0% and not encountered gene HLA-A28 in 0% of cases.
Leading by importance frequency of occurrence genes among patients with multiple myeloma kirghiz nationality and compared with control group it is genes HLA-A25, HLA-A28 , the genes HLA-B7, HLA-B13 and which have statistically highly significant differences P <0.001.
Table 1.
Comparison of HLA alleles II class locus DRB1* multiple myeloma patients and healthy potential donors bone marrow kirghiz nationality
|
HLA- locus DRB1* |
donors kirghiz nationality п = 78 |
patients with multiple myeloma kirghiz nationality п = 22 |
|
0901 |
0,13% |
20% р < 0,003 |
|
1001 |
0,05% |
10% р < 0,04 |
|
1401 |
0,28% |
20% р < 0,04 |
|
1601 |
0,005% |
20% р < 0,005 |
In the allocation of antigens HLA-class II alleles locus DRB1* data which are presented in Table 1, shows, that in most patients with multiple myeloma kirghiz nationality, more encountered genes HLA -DRB1* 0901, HLA-DRB1*1401, HLA-DRB1* 1601 and more rarely encountered HLA-DRB1* 1001 as compared with healthy donors kirghiz nationality and have highly statistically significant differences.
In healthy donors kirghiz nationality found genes HLA-DRB1* 0901 in 0,13% of cases, HLA-DRB1* 1401 of 0,28% and practically in few cases there are encountered gene HLA- DRB1 * 1001 in 0,05% and gene HLA-DRB1* 1601 in 0,005% cases.
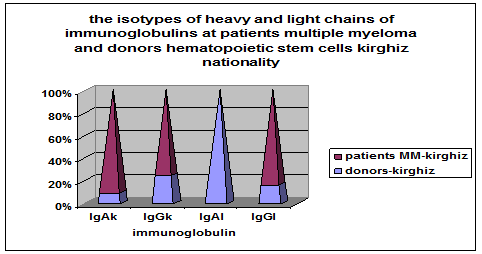
Figure 2. The isotypes of heavy and light chains of immunoglobulins at patients MM and donors hematopoietic stem cells kirghiz nationality.
At comparison encountered form immunochemical variant immunoglobulins light (k,l) chains showed that in patients with multiple myeloma kirghiz ethnic nation more found option IgAk-chain in 95% of cases, Ig Gk-chain in 80% of cases, Ig Gl-chain 85% cases, do not encountered type Ig Al-chain. At potential donors of hematopoietic stem cells kirghiz nationality IgAk-revealed about 5% of cases, Ig Gk-chain in 20%of cases, IgGl-chain in 15% of cases and IgAl- encountered almost 100% cases.
CONCLUSION:
Thus, in the result of research in the distribution of HLA alleles 1 class, found that the most common in donors kirghiz nationality (ethnic population) in locus A - gene HLA -A24, -A26, in locus B -gene HLA-B7, -B13, more rarely HLA- A25, HLA-B14.
And in system HLA- alleles II class DRB1* locus most common genes HLA- DRB1* 0901, HLA-DRB1*1401.
Characteristic for patients with multiple myeloma kirghiz ethnic nationality in distribution HLA - alleles 1 class in locus A - genes HLA- A24, -A25, -A26 -A28, locus B -genes HLA-B7, B13, -B14, and in the distribution of HLA-alleles II class locus DRB1*, it turned, that in patients with multiple myeloma kirghiz nationality, the most common genes HLA-DRB1* 0901, HLA- DRB1* 1001, HLA-DRB1*1401, HLA-DRB1* 1601.
Given that among patients with multiple myeloma kirghiz nationality more found the Ig Ak-myeloma and Ig G- myeloma with elevated (k, l)chains. From prevention to the investigated donors, where are revealed elevated titers of immunoglobulin Ig A, IgG with elevated (k,l) chains. Donors are in the database of the National Register of hematopoietic stem cells Kirghiziа, but debarred from donorship on the results of analyzes and are under the supervision of a therapist.
The identified differences in the distribution of HLA-alleles should be considered when planning closely related, unrelated bone marrow transplantation in patients with MM and at other malignant diseases.
When planning an unrelated bone marrow transplant needed high-quality selection of the donor, with purpose of prophylaxis in order to prevent posttransplant complications, on the principle of "do no harm nor the patient nor the donor."
Transplantation bone marrow - gives the best results for increasing survival in treatment oncohematologic malignancies.
Although, the frequency of occurrence MM patients more often in old people and because of the variety of comorbidities, regardless of age timely selection of PCT(polychemotherapy) and at the presence of HLA-identical donor recommended transplantation peripheral hematopoietic stem cells.
Baratova D.A., Baratova M.A. IMMUNOGENETIC CHARACTERISTICS OF ANTIGENS HLA-ALLELES OF THE MAJOR HISTOCOMPATIBILITY COMPLEX PATIENTS WITH MULTIPLE MYELOMA AND DONORS HEMATOPOIETIC STEM CELLS. International Journal Of Applied And Fundamental Research. – 2015. – № 2 –
URL: www.science-sd.com/461-24888 (28.02.2026).











 PDF
PDF