About Us
Executive Editor:Publishing house "Academy of Natural History"
Editorial Board:
Asgarov S. (Azerbaijan), Alakbarov M. (Azerbaijan), Aliev Z. (Azerbaijan), Babayev N. (Uzbekistan), Chiladze G. (Georgia), Datskovsky I. (Israel), Garbuz I. (Moldova), Gleizer S. (Germany), Ershina A. (Kazakhstan), Kobzev D. (Switzerland), Kohl O. (Germany), Ktshanyan M. (Armenia), Lande D. (Ukraine), Ledvanov M. (Russia), Makats V. (Ukraine), Miletic L. (Serbia), Moskovkin V. (Ukraine), Murzagaliyeva A. (Kazakhstan), Novikov A. (Ukraine), Rahimov R. (Uzbekistan), Romanchuk A. (Ukraine), Shamshiev B. (Kyrgyzstan), Usheva M. (Bulgaria), Vasileva M. (Bulgar).
Medical sciences
Studies of blood serum were performed by enzyme immunoassay for the detection of antibodies Ig G infection to Helicobacter pylori.
It was found that in practically healthy donors in the study with prophylactic purpose were found in the serum of significant indicators of low, medium and high levels of antibodies Ig G to infection Helicobacter pylori.
More frequently taped low levels at women of ethnic kirghiz and in men most often medium and high levels of Ig G antibodies to Helicobacter pylori. In comparative characterization rarely detected antibodies to H.pylori infection in potential donors kirghiz nationality of comparison with healthy people of the North-West region of the Russian Federation. Negative results taped in the donors kirghiz nationality in 80% of cases, and in the residents of the Northwest region of the Russian Federation in 20% of cases.
Given the latent carrier of H. pylori infection is necessary to put the issue of timely quality selection of potential donors of hematopoietic stem cells.
When planning unrelated transplant bone marrow, necessary to consider should to improve the algorithm security of bone marrow.
This allows us to investigate with prophylactic purpose for the selection donors, and the early detection of infection, and timely treatment.
Key words: Helicobacter pylori, carcinogenesis, кirghizs, donors, prevention.
Introduction:
Currently to topical explore the potential bone marrow donors on infection Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) at ethnic peoples and nationalities living in different geographical regions. Helicobacter pylori infection plays a role in the development of tumor process "human carcinogen" and factor is deeply involved in the genesis of cancer and gastric-lymphoma MALT- type and significant role in the occurrence erosive gastritis, of gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer.
The colonization of the gastric mucosa infection Helicobacter pylori accompanied by with followed by the development of chronic gastritis, which at some patients evolves toward a disease or gastric cancer [2].
According data the author [1], in Kirghiz Republic the incidence cancer of stomach greatly is high and he went to first place in the structure of cancer among the of Countries Independent States.
It is generally known that Helicobacter pylori produces a large amount of enzyme urease. The Bacterial urease decomposes on urea in the stomach to carbon dioxide and ammonia [6].
According to the authors in the paper [3], describes epidemiological studies that the proportion of cancer cases are associated with Helicobacter pylori, and therefore potentially preventable through eradication therapy is from 60 to 90%. This allows you to predict the possibility of a significant reduction in morbidity and mortality in populations with high levels of Helicobacter pylori infection combined with a high incidence of gastric cancer.
To date, the existing methods of diagnosis H. pylori infection include invasive and noninvasive studies. Invasive methods are painful and require multiple samples to achieve adequate sensitivity.
In [5] are described according to the recommendations of the 4-th Maastricht 2012 consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of infection H.pylori, where there is a urea breath test using 13C urea, which remains the best non-invasive of tests for the diagnose infection H.pylori. Firstly, it has high accuracy and is easy to perform.
The authors in work [7] describes, that for the test applied 13C diagnostic kits, which possess a no radioactivity.
As well as in [4] describes that the use more in the clinically practice HELIK® test, which relates to non-invasive diagnosis of respiratory infections Helicobacter pylori.
Designed serological tests "ImmunoComb" possess a sufficient specificity and recommended for the serological monitoring infection H. pylori. However, on the early phases of targeted research for infection Helicobacter pylori are rare and the disease often becomes chronic.
Therefore, the aim of this work was to identify the latent infection by immunosorbent assay detection the numder antibodies of IgG to Helicobacter pylori infection at the voluntary bone marrow donors kirghiz nationality.
Materials and methods:
Carried out Investigations on determine the amount antibodies of IgG to Helicobacter pylori infection with a variety of chronic diseases in potential donors hemopoetic stem cell. Heredity in the examinees is not burdened. The studies were conducted in the laboratory of bacterial respiratory infections city St. Petersburg, NHIEM name L. Pasteur from 2005 to 2015 year.
The study group included 80 potential voluntary bone marrow donors kirghiz nationality from National Register of hematopoietic stem cells Kirghizia in St. Petersburg. Investigated 80 sera from donors kirghiz nationality, aged 18 to 50 years, of them 17 women and 63 men, who are residents of city St. Petersburg.
The data were compared with the control group - 79 healthy residents of the North-West region of the Russian Federation, Saint - Petersburg.
Determination of the amount antibodies of Ig G to Helicobacter pylori
In order to determine the amount of Ig G to Helicobacter pylori by enzyme immunoassay, analysis expressed in international units, was used in this test-system"ImmunoKombII H. pylori Ig G».
The results were evaluated on a scale attached to the test sisteme. On antibody levels serum distributed by the respective groups.
0-19.U / ml- negative
20-39 U / ml - a low level of antibodies
40-90 U / ml - the average (middle) levels of antibodies
91-120 or more U / ml- high levels of antibodies
Statistical analysis of the results include the analysis of the standard criteria. X2-square was used to assess significant differences in the incidence of certain characteristics between the control group and a group of donors Definition the value of "p", the corresponding value found. X2-is the square, it was conducted in a computer program based on one degree of freedom.
All mathematical calculations and a general statistical analysis of the study was performed using a personal computer using the application package programs for spreadsheet - "Microsoft - ExcelM version 7.0 for Windows 95, for Windows-2010, Statistica-5.
Results and discussion:
In carrying out by us research on the define amount of Ig G to infection Helicobacter pylori, voluntary donors they considered themselves practically healthy people and clinical manifestation is not detected. However, it turned out in the anamnesis with childhood suffering chronic tonsillitis, chronic gastritis in remission, chronic bronchitis(smokers), chronic sciatica, chronic pyelonephritis in remission and from food allergy.
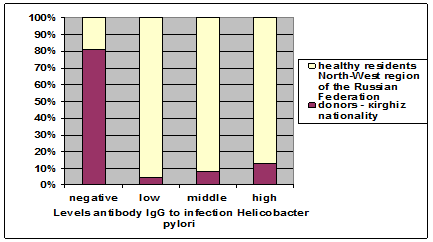
Figure 1. Detection frequency of antibodies Ig G to Helicobacter pylori infection in the donors кirgiz nationality and healthy residents of the North-West region of the Russian Federation.
At comparative characteristic on contents serum levels antibodies of IgG to infection Helicobacter pylori shows that among potential donors of kirghiz nationality is detected negative results in 80% of cases, among residents of the North-West region of the Russian Federation in 20% of cases. Almost low levels contents antibodies of IgG to infection Helicobacter pylori detected in
97.0% of cases among residents of the North-West region of the Russian Federation and in 3% of cases identified during our research among potential donors of kirghiz nationality.
Detected middle level of antibodies among donors kirghiz nationality in 8% and among the inhabitants of the North-West region of the Russian Federation in 82% of cases.
High levels of antibodies revealed among donors kirghiz nationality in 12% and among the inhabitants of the North-West region of the Russian Federation in 88% of cases, these results are presented in figure 1.
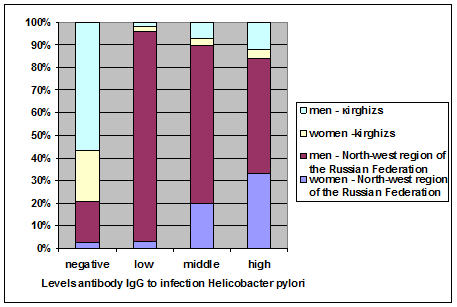
Figure 2. Comparative characteristics of the frequency propagation of the content levels antibodies Ig G infection to Helicobacter pylori among women and men residents the North-West region Russian Federation and potential donors kirghiz nationality hematopoietic stem cells.
As seen from represented figure 2, shows, that at the allocation the donors in analyzes negative content levels antibodies of Ig G to Helicobacter pylori infection found among women residents of the North-West region of the Russian Federation in 3% and among men in 17% cases and in potential donors of hematopoietic stem cells of the kirghiz nationality in women 22% and at men in 58% of cases.
Low levels of antibodies are detected among women in 4% and at men in 92% of cases among residents of the North-West region of the Russian Federation and among donors of kirghiz nationality. at women in 2% and at men 2% of cases.
Detected middle levels of antibodies at women in 20% and at men in 69% of cases among residents of the North-West region of the Russian Federation and among men kirghiz nationality nearly in 9% and practically in unit cases in 2% cases among donors women kirghiz nationality.
High levels of antibodies detected at women in 29%, at men in 51% of cases among residents of the North-West region of the Russian Federation and among donors kirghiz nationality in women 3% and at men in 17% of cases.
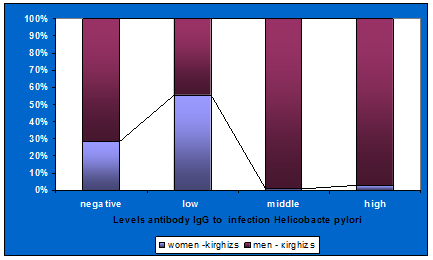
Figure 3. The incidence propagation infection of Helicobacter pylori among potential donors of kirghiz nationality.
As seen from submitted figure 3 shows, that the negative content of the levels of antibodies Ig G to Helicobacter pylori infection are found among ethnic kirghiz potential donors of hematopoietic stem cells at men in 72% and women in 28% of cases, are detected low levels of antibodies at women in 46% and at men in 54% of cases, the middle levels of antibodies in men in 99, 9% of cases in women identified practically in unit cases 1%, detected the high levels antibodies at women in 3% and at men in 99.7% of cases and there are statistically highly significant difference p<0.001.
Thus, on the basis of the above on the moment study, clinically carrier it was not shown.
From gastroscopy the donors suffering from gastritis categorically refused.
Donors are in the database of the National Register of hematopoietic stem cells as the debarred of the donation stem cell, how carriers of H. pylori infection and are under the supervision of physician therapist and gastroenterologist.
Voluntary donors with high levels content of antibodies Ig G to infection H. pylori, require further examination and observation at the therapist and gastroenterologist.
When planning unrelated transplantation is necessary to improve security algorithm bone marrow donor.
In the future, necessary to include in the list of studies determination of antibodies Ig G to Helicobacter pylori at donors in the planning of a bone marrow transplant.
The findings are the basis for the recommendations in-depth survey donors with the aim of right their selection in planning unrelated, closely related transplantation. to bone marrow.
Conclusions:
1.In order to achieve maximum safety when planning unrelated transplantation bone marrow, is
optimal the typing of the antibodies immunoglobulin Ig G to Helicobacter infection pylori with prophylactically.
2. In potential donors bone marrow kirghiz nationality compared with women, most often among men revealed low, and average, and high levels antibodies Ig G to infection Helicobacter pylori. In an initial stage at available chronic gastritis and of antibodies to H. pylori infection should be carried out EGDSkopiya with biopsies.
3. The donors with high levels antibodies of IgG to infection Helicobacter pylori, you need in-depth study EGDSkopiya with biopsies (maximum up to five different locations) and to identify the genetic material of the pathogen
4. In the hereinafter donors with low, medium and high levels of antibodies Ig G to infection H. pylori necessary observation and treatment by a therapist and a gastroenterologist.
Baratova D.A., Baratova M.A. CLINICAL-DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION CONTENTS LEVELS ANTIBODY IMMUNOGLOBULIN IGG TO INFECTION HELICOBACTER PYLORI AND PROSPECTS OF THEIR USE IN POTENTIAL DONORS BONE MARROW. International Journal Of Applied And Fundamental Research. – 2015. – № 2 –
URL: www.science-sd.com/461-24891 (28.02.2026).











 PDF
PDF