About Us
Executive Editor:Publishing house "Academy of Natural History"
Editorial Board:
Asgarov S. (Azerbaijan), Alakbarov M. (Azerbaijan), Aliev Z. (Azerbaijan), Babayev N. (Uzbekistan), Chiladze G. (Georgia), Datskovsky I. (Israel), Garbuz I. (Moldova), Gleizer S. (Germany), Ershina A. (Kazakhstan), Kobzev D. (Switzerland), Kohl O. (Germany), Ktshanyan M. (Armenia), Lande D. (Ukraine), Ledvanov M. (Russia), Makats V. (Ukraine), Miletic L. (Serbia), Moskovkin V. (Ukraine), Murzagaliyeva A. (Kazakhstan), Novikov A. (Ukraine), Rahimov R. (Uzbekistan), Romanchuk A. (Ukraine), Shamshiev B. (Kyrgyzstan), Usheva M. (Bulgaria), Vasileva M. (Bulgar).
Teaching science
The main task of the contemporary secondary general and professional educational systems is to provide the society with highly qualified, competitive, physically and morally healthy profession- nals capable of the development of their creative potential. The solving of the task requires the creation of certain psychological and pedagogical conditions necessary for the development of potential and creative capabilities of the rising generation and of those who will "sow the reasonable, the good, the eternal" (the line from the poem of N. Nekrasov "To the sowers") - of the educators to be.
One of the important conditions of successful education of such professionals, the development of their personal potential and their health preservation is self-cognition which is inevitably followed by self-cultivation; self-development, self-education; self-fulfillment, self-actualization.
What are the potentials, that are inherent to the person or to the individuality? In the opinion of M.S. Kagan [8], there are five potentials that can be distinguished in the structure of the person. Correlation of these potentials shapes the person:
1) Gnoseological potential of the person is characterized by the volume and quality of information which the person possesses. It consists of the knowledge about the external, natural and social, world, and self-cognition. The acquiring of the information depends on the innate intellect, educational level and practical experience of the person.
2) Axiological potential of the person is shaped by the person's system of value orientations - ideals, life purposes, convictions and directionalities as a unity of the person's awareness and self- awareness.
3) Creative potential of the person is characterized by the person's skills and abilities to act and to do constructive or destructive, productive or reproductive work, that the person has developed on his or her own. It is also characterized by the degree of realizations of the skills in a certain sphere of activity.
4) Communicative potential of the person is shaped by the degree and forms of the person's sociability, the nature and permanency of his or her contacts with other people, the content of the interpersonal communication. The potential is also expressed in the person's social roles.
5) Artistic potential of the person is distinguished by the content and intensity of the person's artistic needs and by the way he or she satisfies them.
In the opinion of M.S. Kagan, the person is shaped not by his or her character, physical qualities or anything else, but by person's knowledge and values; by the object and manner of his or her creative activity; by whom the person communicates with and how; by what are the person's artistic requiremants.
Drawing on the analysis of the research results in psychophysiology [5], psychology [3] and on the I.P. Pavlov's view of a human as a system capable of development and self-development, self-sustaining and even self-enhancing we came to the following conclusions:
1. Personal potential is featured by various capabilities (cognitive, intellectual, communicative, artistic, creative ones), which develop in course of the person's active efforts and draws on his or her inherent abilities and psychological and pedagogical conditions of the educational environment.
2. Each person has an inherent potential of a "thinker" (the 2nd signal-system, left hemisphere's functions) and that of an «artist» - creative personality - (the 1st signal-system, right hemisphere's functions). As a consequence each person possesses the potentialities of self-regulation, self-management, self-development, self-education, self-fulfillment, self-actualization. The development of all of them is in connection with the development of the right and left hemispheres' functions. That is one of the main principles of nature coherent education [].
3. In its turn the development of the "thinker's" and "artist's" potentials aids the development of gnoseological, axiological, communicative, artistic, creative and other potentials of the human.
4. The personal potential and related capabilities can develop throughout all human life starting from birth in process of performance and change of a principal kind of activity, as well as in process of research, project and creative activities.
5. Certain stages of human life are sensitive, i.e. more propitious for the development of particular personal potentialities. First of all it is connected with the maturity of physiological functions and the level of the development the corresponding psychical functions. So education is to be coherent with the nature.
It's especially important to take into account the sensitive periods of personal development at the stages of the preschool and primary school education. Unfortunately it is often not provided and leads to the insufficient development of the rising generation's personal potentials at secondary general school, as well as in the following educational systems and professional spheres.
So the sensitive period of the development of imagination and fantasy is the age range from 5 to 7 years, because by this time children's visual active and image thinking have been developed enough, their intellectual operations - analysis, synthesis, comparison, generalization - are in process of development, and the children already have the experience role playing game.
The sensitive period of operating notions is the age range from 12 to 14 years. The period of the logical thinking development is the age from 10 to 13 years as by this time the child has not only the developed visual active and image thinking, intellectual operations and skills, but also the ability to make conclusions.
The sensitive period of the development of the person in whole is the age range from 18 to 20 years. By this time the human can have fairly developed abilities of self-management, self-development, self-education; psychical cognitive processes - perception, memory, attention, thinking, imagination, speech. Different intellectual abilities develops on their basis, including spatial thinking, intellectual styles for problem viewing and solving, as well as integrative abilities of goal-setting, programming, planning, forecasting the activity's results and others, which can be of high importance in professional activities spheres and life activities of the person in whole.
Drawing on the analysis of the results gained by Russian and foreign philosophers, psycho-logists, educationalists in the research of the human and personality development problems we could identify the theoretical and methodological basis for the development of the person and his or her potential, which involve the implementation of the following components of the educational process:
- anthropo-oriented, system-activity, psycho-didactic-system, psychological-pedagogical approaches;
- the three interconnected components of the integrated process of human development in ontogenesis: socialization - the adoption of social experience and knowledge; individualization - the development of the qualities that distinguish one person from another; personalization - the achievement of personhood;
- the principles of the unity of consciousness, person and activity;
- pedagogically grounded complex of activities and communications, which could provide active interaction of the developing personality with his or her social environment;
- preparation of the human within the current period (through the successful integration) for the transition to the next period in order to prevent the appearance of the conditions for the crisis development of the personality;
- the students' cognition of their own individual psychological personal and intellectual peculiarities, which is the basis for their self-education, self-development, self-fulfillment, self-actualization;
- forming the person's orientation including the development of the students' professional orientation, which is the basis for their psychological readiness for the professional activity, that in its turn facilitates the development of their intellectual, professional, creative abilities and their abilities of self-management, self-development, self-education, self-fulfillment, self-actualization;
In this connection drawing on the system psychological and pedagogical approach [19], the authors developed the conception of the quality of education in secondary general and professional educational systems. The conception is presented in Figure 1.
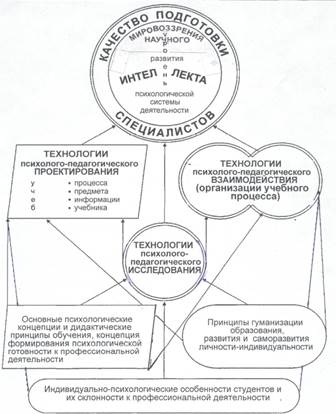
Figure 1. The conception of the quality of education in secondary general and professional educational systems.
According to the conception:
- the education quality of school and professional education institutions graduates (specialists, bachelors and masters) is to be assessed in accordance with the development of their scientific worldview and intelligence, that include their creative abilities and psychological readiness for the activities in the subsequent educational or professional sphere. The quality of education got by the graduates form professional education institutions is to be assessed by their readiness for the professional activities at work;
- the quality of education of the students of schools and professional higher education institutions is provided by the realization of the three groups of psychological and pedagogical technologies in the educational systems. The groups are: research technologies, project technologies and educational process organization technologies. The technologies should implement the principles of humanization of education, of the development, personal self-development, health protection; the main psychological conceptions and didactical principles of education, the conception of psychological readiness of the person for activities, including professional and creative ones.
According to the conception and the results of the analysis of the research performed by the author and doctoral students, working under the author's academic supervision, we distinguished the psychological and pedagogical conditions of the development of the person and personal potential, health protection, quality of education and training in the systems of secondary general and professional education. The conditions include:
- active personal position of students in educational process, their dispositions for self-development, self-fulfillment, self-education based on self-cognition;
- organization of educational process with account of the principles of its congruence with nature and culture;
- efficiency of educational process provided by the educator;
- the construction of creative educational environment, where the person is active and has freedom of actions and activities in knowledge domains and educational systems;
- application of information technologies; didactic, program and methodical educational aids, including electronic textbooks and study packs;
- implementation of the principles of health protection: following the nature and world development lows; harmony with the environment; the harmony of human body, soul and spirit; the principle of search activity; axiological principle; the principle of self-fulfill-ment, self-actualization, self-identification - being own self whatever the circumstances;
Obviously, for to provide the development of students' potentialities, intellectual, professional, creative ones, which characterize the professionals' competitiveness, it's necessary to build the creative educational environment. First of all such environment is to be created in particular subject areas by professional educators drawing on person-centered, system psychological and pedagogical approaches to education - psychodidactcal, activity, context-competency based ones.
What are the principles of construction of the creative educational environment in the school's or higher education institution's educational processes? The main of the principles are reflected in the conception of the quality of education and training of professionals developed by the authors. The principles are to be realized through educational technologies (including the computer ones), forms and methods. The principles include:
- the principles of humanization of education, development, self-development, the protection of personal health of students in educational systems;
- the main psychological conceptions and didactic principles of education, the conception of psychological system of activities;
- the principle of consideration of students' individual psychological features and aptitudes to subject and professional activities (for technical higher education institutions - to engineering and technical or engineering-humanitarian activities).
Besides, for to build the creative environment it's necessary to provide certain psychological and pedagogical conditions for the students' cognitive activity increase, among them are:
- the change of educational process participants' functions: the pedagogue's function is not to transfer knowledge, but to guide the students' cognitive activity. And they are not just passive listeners, but active converters of educational and other information;
- student's motivation for cognitive activity caused primarily by the activity's correspondence with their aptitude to a certain subject or professional activity;
- generalization of educational information by the pedagogue, its structuring and systematization, schematic presentation of the information grouped in blocks: in informational, structural and logical schemes; the schemes providing the orientative basis for actions according to the deductive principle (from the general to the special);
- the appliance of didactic, program and methodical educational mediums; interactive, problem-centered, research, project methods; informational educational technologies;
- joint (in groups-dyads) cognitive activity of students.
It should be noticed that the change of the functions of the educator and students can be possible if the educator develops the didactic material, uses the methods and technologies of realization of the material, system of control in educational process which are capable of providing the active self-consistent cognitive activity of students. This activity should have research, project or creative nature. Such didactic tools can be study packs, including electronic ones.
The study packs and educational technologies aimed at the development of intellectual and professional abilities of students are the didactic and technological support for the creative educational environment in a certain knowledge domain or educational system in whole. Therewith the students acquire the opportunity for active, mostly self-dependent and efficient cognitive work (allowing them to spend less of their time and energy) in a certain knowledge domain. The various educational creative environments built by different authors for a set of disciplines can serve as an example of such environments:
- "Non-organic chemistry" - S.Ju. Andreeva [1];
- "Economy and management of mining" - O.V. Bogdanova [2];
- "Mathematics" in higher education institutions - L.B. Gil' [3], T.V. Tarbokova [23];
- "Mathematics" in the 9th form" - L.M. Golubeva [4], "Mathematics" in the forms from 5th to 11th - A.M. Pustynnikova [14];
- "Literature"in the forms from 5th to 9th - L.S. Mishenina [10];
- "Visual art" at school - V.A. Pantikov [13];
- "Foreign language" at the higher education institution - V.Ju. Zjubanov [6], T.V. Ivanova [7], L.V. Pavlenko [12];
- "Team management inn education" - E.G. Murugova [11];
- "Engineering graphics"- M.V. Matveeva [9]; "Information technologies at professional activity" and other disciplines - N.N. Savel'eva [15];
- «Русский язык и культура речи» - Salosina I,B [16].
- "Hydromechanics"(1994), "Pumps, ventilator, compressor" [17], "Pedagogical psycho- logy" - all the study guides contain structural and logical diagrams - I.Ju. Sokolova [18];
- "Natural science" - Ju.V. Stepanchenko [21], "Ecology" - N.V. Ul'janova [24];
- «Technologies of professional education» - T.N. Tabrosko [22];
- "Theoretical framework for electrotechnics" - N.P. Fiks [25].
The research [17, 20] and pedagogical experience of the author [18,19,] and doctoral students, who work under the author's academic supervision shows that constructing creative educational environment in knowledge domain in different disciplines of secondary general and professional education systems facilitates the development of creative [1,10,13, 14], intellectual [4,14] and other potentialities of students [21,24]; activation and efficiency of students' cognitive activity [6,12,22], development of their intellectual [3], professional [2, 9, 11, 15, 16, 18, 19, 23] capabilities and the protection of their health in secondary general and professional education systems.
At the stage that follows graduation from higher education institution and next stages of life the personal potential development, including qualification upgrade, is performed by the person mainly on his or her own. It's facilitated by the principles of nature and culture coherent education [17, P. 1118-1124] offered by the authors and the health protection principle [19, P. 103-106]. This can be explained in the following way: the implementation of the principles of education coherent with nature (especially in pre-school and elementary education) and with culture at schools, colleges and higher education institutions facilitates the activation and efficiency of cognition and thereby the students' health protection. It also aids the development of the students' gnoseological, intellectual, axiological, creative and other potentials: the development of their world view, consciousness, etc.
Beside, the human can follow the first three principles of health protection - following the laws of the development of nature and world; the harmony with the environment; the harmony of human body, soul and spirit, - if the human has a sufficiently developed world view and consciousness.
Along with it the person actively cognizes the world and develops and by his or her development aids the development of everything that surrounds him or her. Thereby the person protects and strengthen his or her health. Another four principles are: search activity principle, axiological one, self-fulfillment and self-actualization, self-identification and sellf-sufficiency principles. They implement if the person's cognitive activity is research or project one, or creative one in general.
The psychological and pedagogical conditions of the development of students' personal potential offered by the author can be applied to the process of upgrading of pedagogical cadres qualifications or that of the retraining of professionals in different spheres, as well as to professional pedagogical work in certain knowledge domains (see the references below).
2. Bogdanova O.V. Theoretical study and methods of teaching economy to polytechnic students. Abstract of thesis cand. of ped. sci. . Tomsk: TSPU, 2005.
3. Gil L.B. The development of intellectual skills and the ability of self-development of the technical higher education institution students in process of mathematical education. Abstract of thesis cand. of ped. sci. Tomsk, 2010. 23 p.
4. Golubeva L.M. Tutorial set as a means of students intellectual development (based on the example of a math class). Abstract of thesis cand. of ped. sci. . Tomsk: TSPU, 2001. 18 p.
5. Golubeva E.A. Abilities and individualism. Moscow, Prometey Publ., 1993. 305 p.
6. Zyubanov V.Yu. Independent cognitive work activation in the process of foreign language acquisition on the basis of a computer set. Abstract of thesis cand. of ped. sci. Tomsk: TSPU, 2007. 22 p.
7. Ivanova T.V. Individually oriented system of foreign language training of the technical higher educational institution’s students. Abstract of thesis cand. of ped. sci. Tomsk. TSPU, 2003. 20 p.
8. Kagan M.S. Human activity: (the experience of system analysis). Moscow, Politizdat Publ., 1974. 328 p.
9. Matveeva M.V. Students training activation relevant to design engineering activity by means of IT (based on the examples of engineering graphics). Dis. cand. of ped. sci. . Krasnoyarsk, 2003. 22 p.
10. Mishenina LS. Personally oriented system of enhancing cognitive and research activities of schoolchildren of the forms from 5th to 10th. Abstract of thesis cand. of ped. sci. Tomsk, 2005.18 p.
11. Murbgova E.G. The preparation of education managerial cadres for team management in the system of advanced professional training. Abstract of thesis cand. of ped. sci. Tomsk, 2013. 24 p.
12. Pavlenko L.V. Optimization of the foreign language training of law students. Abstract of thesis cand. of ped. sci. Tomsk, 2007. 22 p.
13. Pantikov V.A. Didactical conditions of the development of imagination and artistic creation
abilities of the elementary school students at visual art lessons. Abstract of thesis cand. of ped. sci. Tomsk, 2003. 18 p.
14. Pustinnikova A.M. Didactic repetitions as a means of students combinatorial skills development (5-11 forms). Abstract of thesis cand. of ped. sci. . Tomsk: TSPU, 2004.
15. Saveleva N.N. . The training of the intended bachelors of mechanical engineering for their professional activity at high technology mechanical engineering enterprises. Abstract of thesis cand. of ped. sci. Tomsk, TSPU, 2015. 24 p.
16. Salosina I.V. Development of a text competence (prospect teachers). Abstract of thesis cand. of ped. sci. . Tomsk: TSPU, 2007.
17. Sokolova I.Yu. The conception of nature and culture coherent education. The issue of the RAE: Fundamental research. 2013, no. 8 (10), pp. 1818-1824.
18, Sokolova I.Yu. Pumps, ventilators, compressors. Textbook with SLS. Tomsk, TPU Publ., 2016. 114 p.
19. Sokolova I.Yu. Pedagogical psychology: textbook with SLS / Stamped by Academic Methodological Association for professional pedagogical education. Tomsk,TPU Publ., 2013. 328 p.
20. Sokolova I.Yu.. Terehina L.A. Health protection principles as a ground for forming the culture of health of the subjects of educational process in technical higher education institution: the collection of the proceedings of the 10th All-Russian conference “Science and education”. Tomsk, TSPU, 2006. P. 274.
21. Stepanchenko Iu.V. Teachers training for natural science formation based on biospherecentral. Abstract of thesis cand. of ped. sci. . Tomsk: TSPU, 2007.
22. Tabrosko T.N. Psychologic-pedagogical conditions for skills development of prospect teachers. Abstract of thesis cand. of ped. sci. Tomsk, TSPU, 2006.
23. Tarbokova T.V. Didactic system of activating students’ cognitive as a means of the enhancement of their mathematical preparation efficiency. Abstract of thesis cand. of ped. sci. Tomsk, TSPU, 2009. 25 p.
24. Ulianova N.V. Pedagogical conditions of forming ecological culture of schoolchildren of forms from 5th to 11th. Abstract of thesis cand. of ped. sci. . Tomsk: TSPU, 2007. 22 p.
25. Fiks N.P. Theoretical study and experience of educational set application. Abstract of thesis cand. of ped. sci. . Tomsk: TSPU, 2002.
Sokolova I.Yu., Borisova E.E. PERSONAL POTENTIAL AND ITS DEVELOPMENT IN PROCESS OF HUMAN LIFE. International Journal Of Applied And Fundamental Research. – 2016. – № 1 –
URL: www.science-sd.com/463-24977 (31.01.2026).











 PDF
PDF