About Us
Executive Editor:Publishing house "Academy of Natural History"
Editorial Board:
Asgarov S. (Azerbaijan), Alakbarov M. (Azerbaijan), Aliev Z. (Azerbaijan), Babayev N. (Uzbekistan), Chiladze G. (Georgia), Datskovsky I. (Israel), Garbuz I. (Moldova), Gleizer S. (Germany), Ershina A. (Kazakhstan), Kobzev D. (Switzerland), Kohl O. (Germany), Ktshanyan M. (Armenia), Lande D. (Ukraine), Ledvanov M. (Russia), Makats V. (Ukraine), Miletic L. (Serbia), Moskovkin V. (Ukraine), Murzagaliyeva A. (Kazakhstan), Novikov A. (Ukraine), Rahimov R. (Uzbekistan), Romanchuk A. (Ukraine), Shamshiev B. (Kyrgyzstan), Usheva M. (Bulgaria), Vasileva M. (Bulgar).
Engineering
The operating conditions to control the degree of the environmental impact of diesel locomotives on the environment held special periodic tests with the assessment of the composition and the specific amount of harmful emissions in the exhaust gases at various loads of diesel generator diesel units. Then the mass value of the emissions of harmful substances when i work the locomotive for some interval time t defined for formula kg
where Пk - the number of driver controller positions of the locomotive; gik - specific emission i harmful substances while working on the locomotive driver controller positions k, kg/h; tk- time locomotive at position k, h.
Despite the existence of experimental methods for monitoring environmental parameters of transport engines, it must be assumed that the most reliable, most accurate, most affordable and less time consuming methods are analytical estimates of the number of products of combustion, which are based on the reactions of the components of fuel oxidation by atmospheric oxygen.
For the calculation of operational environmental performance of production of diesel engines can be used a method of equilibrium composition [1], the benefits of which are obvious for the following reasons:
- in the calculation of the combustion products is taken into account the elemental composition of hydrocarbon fuel;
- the composition and the number of elements in the combustion products is calculated using the thermodynamic parameters of the working fluid (the proportion of unburned fuel, pressure, temperature, cylinder volume, excess air ratio, etc.) in the process of burning fuel;
- the results of mathematical modeling of the parameters of the internal combustion engine working cycle, which is based on the results of bench tests determined the combustion efficiency in the cylinder, which is adjusted on the basis of the composition and quantity of the products of combustion.
According to [2] we accept that, as a part of the exhaust gases from the combustion of diesel fuel composition of H + C + O + S = 1 may contain 36 elements for the definition of the amount - which uses four material balance equations written in the form:
![]()
(2)
![]()
(3)
![]()
(4)
![]()
(5)
Dalton's equation
![]()
(6)
where n - number of elements in the diesel fuel combustion products;![]() - number of atoms of the corresponding elements in the flue gas.
- number of atoms of the corresponding elements in the flue gas.
The number of atoms of the corresponding elements in the equations (2-5) are expressed in terms of the partial pressure of the corresponding thermodynamic state of the working fluid in the engine cylinder.
The values of the partial pressure of combustion products i to j phase of combustion are determined by joint decision of the equations (2-6) before calculating equilibrium dissociation constant during the reaction of gaseous combustion products that the ratio of the partial pressures of the individual components of the mixture.
The magnitude of the partial pressures of the individual components is determined by combustion at a known temperature, using the combustion gas dissociation equilibrium constants of the reactions [2].
![]()
(7)
where X = Tzj / 1000 - temperature working fluid in the cylinder j in the time of fuel combustion, K; K0, K1 , ... , K10 - equilibrium constants of reactions of gases dissociation .
Then the number of the i - th combustion product to of j - th moment mij combustion process is determined by using the equation of state of gases, kg:
![]()
(8)
where mi - molar mass of i- product of combustion , kg/kmol; Vj, Tj - the volume of the cylinder and the working temperature of the body in the j - th point of the combustion process ; R - universal gas constant.
Sequential combustion summation quantity at time intervals (crank angle) from the beginning of the products of combustion (j = 0) to the end (j = jz) to determine the number of i - th combustion product and the total amount of exhaust gas during the operating cycle of the engine:
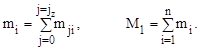
(9)
Changing the working fluid parameters (volume, pressure, temperature, and the proportion of fuel combusted air-fuel ratio) in the cylinder to the estimated time interval ji-1- ji is due to heat generation during combustion, heat exchange with the working fluid cylinder walls, gas exchange between the volume cylinder intake and exhaust systems, changes in the composition of the working fluid etc.
In calculating the operational environmental performance of production process parameters of transport diesel fuel burning in the engine cylinder can be estimated using the equation I.I. Vibe [4,5].
Using the method of equilibrium composition and process parameters of fuel burning in the cylinder calculated by the method of I. Vibe [3,4,5], determined the amount of the combustion products of diesel 6CHN31,6/33 for nominal operation (Table 1).
The table does not include the products of combustion, the quantity of the exhaust gases which does not exceed 10-20 kg/h is methane, nitrogen sulfide, methine, methylene, ethynyl and other elements.
Table 1. Number of fuel combustion in a diesel engine 6CHN31,6 / 33 for the nominal mode
|
Name of product combustion
|
Number of products combustion , kg/h |
Name of product combustion |
Number products combustion , kg/h |
|
Oxygen О2 |
8,9095×102 |
Oxides of nitrogen NО |
5,5976×100 |
|
Ozone О3 |
1,2247×10-5 |
Nitrous acid nitrogen NO2 |
0,3789×100 |
|
Hydrogen Н2 |
2,1444×100 |
Cyan CN |
2,2123×10-18 |
|
Hydroxyl ОН |
5,6553×10-2 |
Formyl НСО |
1,3984×10-11 |
|
Aqua Н2О |
9,6511×101 |
Formaldehyde Н2СО |
4,6094×10-15 |
|
Сarbon dioxide СО2 |
2,4588×102 |
Ammonia NH3 |
1,2539×10-10 |
|
Сarbon monoxide СО |
6,6939×10-4 |
Ammonocarbonous acid HCN |
1,2330×10-16 |
|
Monatomic carbon С |
0,1750×100 |
Diatomic sulfur S2 |
1,4528×100 |
|
Diatomic nitrogen N2 |
4,7558×103 |
Sulfur oxide SO |
1,3344×10-15 |
|
Monoatomic nitrogen N |
1,0542×10-10 |
Sulphurous acid anhydride SO2 |
1,7553×10-9 |
|
Note. Power diesel Ne = 883 кВт, Specific fuel consumption be = 0,278 кг/(кВт·ч). |
|||
Conclusions
Thus, the use of mathematical models to assess changes parameters of fuel burning in the engine cylinder and the method of calculation of the combustion products at equilibrium conditions, will eliminate the gas analyzers ensure the efficiency of environmental control, to evaluate the technical condition of vehicles and engines of the quality of the flow of the working process in the cylinder.
2. Minitaeva A.M. Information and communication technologies as the instrument of eco-logical regulation of harmful substances in the atmosphere // Slavic forum. 2015. №2(8). P. 194-200.
3. Minitaeva A.M. Information - communication technologies as a tool to regulate the emissions on the atmosphere of pollutants // Proceedings of the Plekhanov Russian University of Economics. 2015. № 3 (21). С. 69-74.
4. Minitaeva A.M., Skovorodnikov E.I., Akhmetov S.I., Mathematical model for the com-parative monitoring of environmental safety diesel - tion engines // Dynamics of systems, mecha-nisms and machines. 2009. № 3. P. 412-414.
5. Skovorodnikov E.I., Ovcharenko S.M., Minitaeva A.M., Nekrasov I.V. A mathematical model for calculating the fuel consumption rate of diesel locomotives for hauling // Herald Omsk Scientific. 2006. № 8 (44). P. 97-103.
Minitaeva A.M. METHOD OF ANALYTICAL CONTROL OF THE COMBUSTION TRANSPORT DIESEL ENGINES. International Journal Of Applied And Fundamental Research. – 2016. – № 1 –
URL: www.science-sd.com/463-24978 (12.03.2026).











 PDF
PDF