About Us
Executive Editor:Publishing house "Academy of Natural History"
Editorial Board:
Asgarov S. (Azerbaijan), Alakbarov M. (Azerbaijan), Aliev Z. (Azerbaijan), Babayev N. (Uzbekistan), Chiladze G. (Georgia), Datskovsky I. (Israel), Garbuz I. (Moldova), Gleizer S. (Germany), Ershina A. (Kazakhstan), Kobzev D. (Switzerland), Kohl O. (Germany), Ktshanyan M. (Armenia), Lande D. (Ukraine), Ledvanov M. (Russia), Makats V. (Ukraine), Miletic L. (Serbia), Moskovkin V. (Ukraine), Murzagaliyeva A. (Kazakhstan), Novikov A. (Ukraine), Rahimov R. (Uzbekistan), Romanchuk A. (Ukraine), Shamshiev B. (Kyrgyzstan), Usheva M. (Bulgaria), Vasileva M. (Bulgar).
Chemical sciences
In recent years there is considerable interest in composite materials based on polymer matrices and nano-sized particles of metals, due to their wide range of applications- from catalysis to nanotechnology in information technology and in many areas of chemistry, physics and material science [6].There are works on obtaining of mixed thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) and dynamically vulcanized thermoplastic elastomers (TPV) with isotactic polypropylene (PP) as thermoplast, and ethylene propylene diene elastomer (EPDR) or butadiene nitrile rubber (BNR) as elastomers using various fillers or compatibilizators to improve compatibility as well as physical-mechanical and technological properties of the compositions [2,4,8].The use of solid nanoparticles (NP) of different chemical nature as fillers for polymeric materials opens new possibilities for modifying of the last ones since the surface properties of nanoscale substances have a high surface energy and adsorption activity [5]. Previously, we have derived new TPE based on PP/EPDR using nanofillers (NF) containing copper oxide NP. It is shown that the introduction of NP into TPE leads to an increase of temperature of the beginning of thermooxidative destruction maintaining mechanical characteristics of TPE [3]. In the presented work we investigated the properties of mixed TPE and dynamically vulcanized TPV based on isotactic PP and EPDR with the use of NF containing NP oxides of various metals, stabilized in polymer matrices.
Experimental
|
*This work is supported by a grant (Project Number: SDF-Mob-1-2013-1(7)-16/13/4) from Scientific Development Fund by the President of Azerbaijan Republic |
In the work used: isotactic polypropylene (PP) of brand 21030-16 (Russia) with Мn=7.7х104 and Mw=3.4xl05; density r=0.907 g/cm3; the degree of crystallinity of 55%; melting temperature Tm=165°C; MFR=2.3 g/10 min at T=190°C and a load of 2.16 kg; EPDR brand Dutral TER 4044 with the number of propylene units 35%, a Mooney viscosity of 44 (100°C); In the composition EPDR diene component was 5 ethyliden-2-norbornene in the amount of 4-5%. As NF used metal oxides NP stabilized on polimer matrix: NP of copper oxide I (Cu2O), NP of nickel oxide (NiO) were stabilized in the matrix of polyethylene obtained with the use of titanium-phenolate catalytic system (NPCuPE), (NPNiPE), NP of copper oxide I (Cu2O) on the matrix of acrylonitrilebutadiene thermoplaste (NPCuABS) and NP of iron oxide (Fe3O4) on the matix of DSR-divinylstyrene elastomer (NPFeDSR) in an amount of 1 mass.p. on a polymer mixture.The NP content in the polymer matrix: NP of copper oxide - 3.9%, NP of nickel oxide -18%, and NPFeDSR -30%, NP size: NPCuPE, NPCuABS and NPNiPE 11-15nm, NPFeDSR -100nm, the degree of NP crystallinity is 25-45%.The ratio of initial components(mass.p.):PP/EPDR/NF=50/50/1.
Polymer composites are obtained by mixing in a high-speed mixer "Brabender" at T=190°C and a rotor speed of 100 rpm for 10 min, and vulcanized by the method of dynamic vulcanization in the same conditions with the use of sulfur-cure system, which was comprised of the following ingredients (in mass. p. on 100 wt. p. of rubber): sulfur 1.0, zinc oxide 2.5, stearic acid 1.0, altax 0.25, thiuram 0.7. Samples for the study were obtained by hot pressing in the form of plates with thickness 0.35 mm at 190°C and a pressure of 10 MPa for 10 min with subsequentcooling to room temperature at a rate of 20°C/min.
To study the mechanical characteristics of mixtures, from compression molded plates were cut samples in the form of blades with dimensions 35.00x5.00x0.35 mm. Uniaxial tensile tests of samples were performed on a testing machine "Instron-1122" at room temperature and a constant rate of movement of the upper traverse 50 mm/min. Rheological measurement was carried out under constant load at 190°C on the capillary microviscosimeter IIRT-5 and loads of 2.16, 5.00, and 10.6 kg. Thermal and thermo-physical properties of the obtained nanocomposites was investigated on the instrument "Thermoelectron Corporation" firma (USA) 2006, Q-20-DSC. The research is conducted in the atmosphere of nitrogen or air at a heating rate of 10°C/min. X-ray phase analysis of the compositions is performed on the device "D2 Phaser" of Bruker (Germany). The measurement of dielectric properties of the obtained materials was carried out using a measuring complex Concept 40 from firm Novocontrol, (Germany).The measurement accuracy of the dielectric permittivity is 0.01, of dielectric loss is 1x10-5.The measurements were performed at a room temperature, limiting frequency range to 0.01 Hz -10-6 Hz.
Results and discussion
The new nanocomposites based on PP/EPDR with the use of NP oxides of copper, nickel and iron were obtained.The researches of physical-mechanical, electrical, phisical-thermal, and thermal properties, as well as the X-ray analysis of the obtained nanocomposites were performed. In the table 1 presented parameters of nanocomposites TPE and TPV, containing NF with NP oxides of various metals.
Table 1. The properties of analyzed TPE and TPV.
|
composition |
Е, МPа |
σр, МPа |
εр, % |
MFR, g/10мин, Т=190˚С |
έ1 |
К,% |
||
|
2.16kg |
5.00 kg |
10.60kg |
||||||
|
Non-vulcanized TPE |
||||||||
|
PP/EPDR |
395 |
11.0 |
170 |
0.9 |
3.7 |
14.8 |
2.0 |
53.7 |
|
PP/EPDR/NPСuPE |
260 |
9.3 |
150 |
1.1 |
4.3 |
18.0 |
2.2 |
49.9 |
|
PP/EPDR/NPNiPE |
263 |
8.7 |
110 |
1.1 |
4.4 |
16.8 |
2.2 |
50.2 |
|
PP/EPDR/NPCuABS |
269 |
8.6 |
110 |
1.0 |
4.0 |
16.2 |
1.7 |
50.7 |
|
PP/EPDR/NPFeDSR |
201 |
7.6 |
40 |
1.2 |
4.6 |
16.8 |
2.4 |
50.0 |
|
Dynamically vulcanized TPV |
||||||||
|
PP/EPDR |
215 |
13.2 |
370 |
- |
- |
- |
2.0 |
49.4 |
|
PP/EPDR/NPСuPE |
165 |
14.0 |
390 |
- |
- |
0.15 |
2.1 |
52.1 |
|
PP/EPDR/NPNiPE |
114 |
12.8 |
340 |
- |
- |
- |
2.4 |
50.0 |
|
PP/EPDR/NPCuABS |
115 |
12.0 |
350 |
- |
- |
- |
2.4 |
54.8 |
|
PP/EPDR/NPFeDSR |
142 |
7.5 |
100 |
- |
- |
- |
2.1 |
51.6 |
E - modulus of elasticity, σр - tensile strength, εр - elongation at break, MFR- index of the melt flow,
K- crystallinity, έ1 - dielectric constant
As can be seen from table 1, mixed in TPE application of NN leads to some reduction of the modulus of elasticity at a certain preservation of the strength parameters of the system, however, increases the rate MFR under a load 10.6 kg 1.22 times. The application of NN in the vulcanized compositions - TPV leads to the decrease of the modulus of elasticity E in 1.3 times, while maintaining the tensile strength and percentage elongation.The system is not flowing with loads of 2.16 and 5.0 kg, and the load increase to 10.6 kg leads to the appearance of flow of the mixture (in the case of NPCuPE), which is crucial for processing of the system.
The decrease in the elasticity modulus of the composite,is probably due to aggregation of the NP, resulting in the formation of microdefects in a polymeric matrix.The appearance of the flow of the composite, apparently, is connected with increase in the mobility of polymer segments in the interaction of NP with the matrix at the nano-level.
The effect of NF containing NP of metal oxides on the structure of the obtained TPE was investigated using X-ray-analysis method. Diffractograms X-ray confirm the presence of nanoparticles of copper oxide in thethermoplastic elastomers: dhkl 3.02053; 2.46466; 2.13683; 1.74331; 1.51025; 1.28812 Å, which corresponds to the ASTM card index number dhkl series of copper oxide (I)- Cu2O; reflexes that are characteristic for Nickel-containing nanoparticles : dhkl 1.48525; 2.10037; 2.42535 Аº, which corresponds by the ASTM card index to the series of nickel oxide (NiO) and reflexes that are characteristic for iron-containing nanoparticles dhkl 1.28009; 1.32722; 1.41886; 1.48388; 1.61545; 1.71344; 1.876984; 1.92574; 2.09853; 2.42317; 2.523092; 2.96776; 4.19705; 4.84631 Аº, which corresponds by the ASTM card index to dhkl series of iron oxide (Fe3O4 ).
The study of electrical properties of the obtained nanocomposites showed that the source TPE dielectric constant is έ1= 2.0. When introduced into the composition of the mixtures of NF containing different NP, the value έ1 (1.7-2.4) practically does not change and is constant in the whole studied frequency range.
The values έ1 obtained for the studied mixed and dynamically vulcanized TPE correspond to the data for normal dielectrics. The study of crystallinity of the obtained nanocomposites showed that the dynamic vulcanization of a mixture of PP/EPDR slightly lowers its crystallinity K from 54 to 49%, while the introduction NP of different nature practically does not affect the crystallinity of the studied TPE and TPV.
The DSC thermograms showed that the introduction of different NP in TPE virtually has no effect on the melting point of the mixtures (162 - 166°C), but increases the temperature of the beginning of thermooxidative destruction (420 - 470°C), indicating a higher thermal stability of the obtained nanocomposites.
As shown by the results of the research , physical-mechanical parameters of the system PP/ EPDR involving NF , containing (NPCuPE)) and (NPNiPE), are higher in comparison with parameters for NF with (NPCuABS). Apparently the difference makes not only the influence of NF, containing different metal oxides, but also the question of compatibility of polymer matrices on which these NP are stabilized, with original analyzed system PP/EPDR, because the same NP of copper oxide, stabilized in a different matrices of PE and ABS, show different values of physical and mechanical properties. It should be noted that the PE is non-polar polymer, and consequently NF containing NPCuPE and NPNiPE fairly well combine with the source system, while ABS is a polar polymer and poorly combine with the source system, therefore the values of physical and mechanical properties of PP/EPDR involving NF, comprising (NPCuABS) are not very low.
The studies results showed that the best properties have the TPE and TPV with NPCuPE. It should be noted that the use of NF containing NPFeDSR, significantly reduces the mechanical characteristics of the TPE and TPV. This is probably due to the fact that the size of the NP(100nm) of this type is quite large, and they introduce additional defects to the structure of the Mixes.
It is shown that the obtained nanocomposite TPE based on PP/EPDR with the use of NFcontaining NP of copper oxides and nickel have improved rheological performance with preservation of tensile strength and percent elongation at a somewhat reduced value of the modulus of elasticity. The application of NF in the vulcanized compositions - TPV leads to the appearance of the mixture flow (only in the case of NPCuPE), which is essential for refining of the system.
In the case of nanocomposite containing NPCuPE, improved properties can be explained by the fact that NP Cu2O partially interacts with the components of the curing system with the formation of the adduct Сu2(НСОО)4 ((СН3)2SO)2, wherein Сu+ is oxidized to Сu2+ . This is evidenced evidenced by the X-ray analysis (Fig.1), as well as the appearance in the IR spectra of absorption bands: 1377сm-1 relating to the fragment ((СН3)2SO)2; 2830сm-1 is characteristic for the group of CH3О-; 1750сm-1, corresponding to the anion СОО-[7].
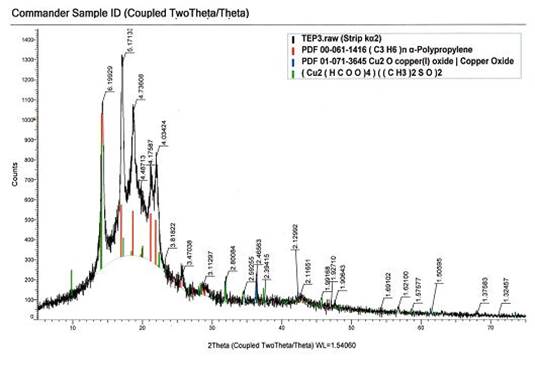
Figure 1. Diffractogram nanocomposite PP/EPDR/NPСuPE
Conclusions
The influence of NF containing NP oxides of various metals on the properties of the mixed and dynamically vulcanized TPE based on isotactic PP and EPDR has been studied. The diffracttograms of X-ray phase analysis confirm the presence of nanoparticles of metal oxides in TPE.
As a result of the conducted researches it is shown that small NF additive in an amount of 1 mass. p. almost has no effect on the crystallinity and dielectric permeability of TPE and TPV, but reduces the modulus of elasticity. The data obtained on the electrical properties of TPE match the performance of conventional dielectrics. The DSC thermograms showed that the introduction of different NP into TPE virtually has no effect on the melting point of the mixtures, but increases the temperature of the beginning of the thermo-oxidative degradation at 30-50°C, indicating a higher thermal stability of the obtained nanocomposites.
The results indicate that small amounts of nanofiller (1.0 mass.p.), injected into the polymer, obviously, play the role of structure-forming agents - artificial nuclei of crystallization, which causes the appearance of the fine spherulitic structure in polymer, characterized by improved physical-mechanical, rheological and thermal properties of the obtained nanocomposite [1,С.80,328].
2. Karpov A. G, Zaikin A.E.. Bikmullin P. C. Elasto-dynamic hysteresis properties of thermoplastic elastomers modified with nanofiller // Vestn. Kaz. Indus. Univ .- 2008, No 5, - P. 124-129
3. Kurbanova N. I., Alimirzoeva N. A., Kuliev A. M., Medintseva T. I., Kuznetsova O.P., Prut E. V. Nanocomposite thermoelastolayers on the basis of isotactic polypropylene and ternary ethylene propylene diene elastomer // European Applied Sciences. -2014, No 4, - P. 100-103.
4. Medintseva T. I., Yerina N.A., Prut E. V. On certain integrals of Lipschitz-Hankel type involving products of Bessel functions // High-molecular compounds. A, -2008, -Vol.50, - P. 998-1098.
5. Mikhailin Y. A. Polymer composite materials // Polymer materials. - 2009, No 7, - P. 10-13.
6. Pomogaylo A.D., Rosenberg A.S., Uflyand I. E. / Nanoparticles of metals in polymers. -M.: Khimiya, -2000, - 672.
7. Tarasevich B. N. / The infrared spectra of the major classes of organic compounds. The reference materials. -M.: Moscow state University, -2012, - P.54.
8. Volfson S. I.., Ohotina N. A., Nigmatullina A. I. et al. Preparation copolymer based functionalized polypropylene and nitrile rubber in the process of mixing.// Plast. mass., -2012, No 4, -P. 42-45
Kurbanova N., Alimirzoeva N. Metal-containing nanocomposites on the basis of isotactic polypropylene . International Journal Of Applied And Fundamental Research. – 2016. – № 4 –
URL: www.science-sd.com/466-25041 (11.02.2026).











 PDF
PDF