About Us
Executive Editor:Publishing house "Academy of Natural History"
Editorial Board:
Asgarov S. (Azerbaijan), Alakbarov M. (Azerbaijan), Aliev Z. (Azerbaijan), Babayev N. (Uzbekistan), Chiladze G. (Georgia), Datskovsky I. (Israel), Garbuz I. (Moldova), Gleizer S. (Germany), Ershina A. (Kazakhstan), Kobzev D. (Switzerland), Kohl O. (Germany), Ktshanyan M. (Armenia), Lande D. (Ukraine), Ledvanov M. (Russia), Makats V. (Ukraine), Miletic L. (Serbia), Moskovkin V. (Ukraine), Murzagaliyeva A. (Kazakhstan), Novikov A. (Ukraine), Rahimov R. (Uzbekistan), Romanchuk A. (Ukraine), Shamshiev B. (Kyrgyzstan), Usheva M. (Bulgaria), Vasileva M. (Bulgar).
Chemical sciences
Abstract
Polymeric dosage forms for sustained release local anesthetics have been developed. Polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan blend films with various compositions were used as polymer carrier. Drug release from polymeric forms is investigated. Drug containing polymeric films shows a high initial release rate and the matrix-controlled release for more 6-8 h. The release data depends on drug loading and polymer structure. The possibility of application of polymeric blends for prolongation of local anesthetics is show.
Key words: dosage forms, drug release, polyvinyl alcohol, chitosan, local anesthetics..
Introduction
Actual problem of modern chemistry of medical polymers is development of polymeric forms of anesthetizing drugs. Principally new polymeric forms are medical films, which placed on wounds and mucous surfaces. The anesthetizing films found the greatest distribution in dental therapy, ophthalmology and treatment of wounds and burns.
Polymeric anesthetizing films represent considerable interest in developing the buccal medicinal forms. Such films when placing on mucous oral cavities are capable to release slowly anesthetizing preparation, providing long local anesthesia. The buccal films with the prolonged release of lidocaine are developed on the basis of gelatin. Influence of properties of gelatin, structure of polymeric composition and its solubility on anesthetic release from films is studied. It is established that at 37оС the release is regulated by dissolution rate, and at 25оС is regulated by diffusion rate. The polymer films received at processing gelatin by formaldehyde, provided diffusive release lidocaine, accepted for the medical purposes [1].
Mucosal dosage form of lidocaine using hydroxypropyl cellulose and carbopol are developed for the purpose of elimination of toothaches. The influence of ratio of polymeric components and drug loading of anesthetic release from the buccal films is shown in vitro conditions. In the conditions in vivo at the placement of films on gum of volunteers it is established that lidocaine adsorption comes from mucosal form for 30% in the first hour and gradually increases by 10% within the next 4 h [2].
The purpose of present work is development of novel polymeric dosage forms for sustained release of local anesthetics. The drug release characteristics of such systems were discussed.
Material and methods
Polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan (PVA/Cs) blend films with various compositions were prepared by following way. The amount of PVA and Cs is filled with distilled water and maintained on magnetic mixer at temperature 80-90°C before full dissolution. The calculated amount of drug added to cooling at room temperature homogeneous polymer solution. After stirring the received solution poured out in glass established horizontally and dried in at room temperature up to constant weight. The received dosage forms had an appearance of thin elastic transparent film from which by means stamp cut out squares 0,2-0,5 mm thick. Calculation of dose of drug was carried out from criterion of the minimum dose. The release behaviour of drug from polymeric samples was examined by means of immersing the disc-shaped samples of 0,3-0,5 mm thickness and 10,0 mm diameter in a Ringer-Lock solution at 37°C. The amount of drug released was determined by UV-spectrometry by measuring the absorption maximum. UV spectra were recorded on a Jasco UV/VIS-7850 (Japan) spectrophotometer.
Results and Discussion
One of the main characteristics of dosage forms is the program of drug release to the organism. The release behavior of local anesthetics from polymeric materials was studied by immersing polymeric samples into model biological media at 37°C. All the release data show the typical pattern for a matrix-controlled mechanism. The cumulative amount of drugs released from the dosage forms was linearly related to the square root of time and the release rate decreased with time. The process is controlled by the dissolution of the drug and by its diffusion through the polymer. The release is described by Fick's law and proceeds by first-order kinetics. The total amount of local anesthetics is released in 6-8 h, the release time for 50% of drug is 2-3 h. Increasing the drug loading from 25 to 100 mg/g resulted in an increase in the drug release rate. Data on drug release from polymeric films are presented in Figure.
Duration of drug release from monolithic therapeutic systems considerably depends on the swelling of polymeric matrix. Dependence swelling degree films from thickness of samples shown that the most optimum properties films 0,4-0,6 mm thick possessed. Such materials swelled for 55-60% within initial 1,5-2,0 h with the subsequent achievement of the maximum value of 80% in 6 h, thicker films very slowly swelled for 45-50% within 1,5-2 h that didn't conform to medical requirements. Release of drug is limited by the rate of swelling and thickness of polymeric matrix.
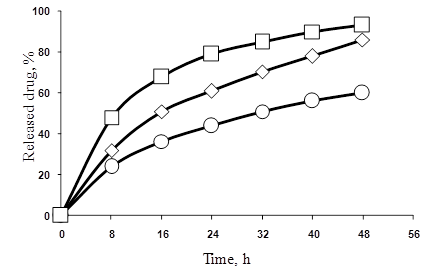
Figure - Release of lidocaine from dosage forms at various drug loading:
25 mg (0), 50 mg (◊), 100 (▫) mg /1 g of polymer
The clinical tests of polymeric dosage forms are conducted at treatment of periodontal pathology. The main advantage of film is long and effective therapeutic effects of small drug doses in the area of pathology. The regulation process is carried out by slow diffusion of oral fluid in polymer, followed by swelling, biodegradation and slow release of the drug from swelling polymer. The sustained drug release from films provides prolonged therapeutic effect. Clinical efficacy was confirmed in statistically significant reduction of terms of treatment of patients with generalized periodontal disease.
Conclusion
Polymer film dosage forms of local anesthetics have been developed. Drug release from polymeric forms is investigated. Drug containing polymeric films shows a high initial release rate and the matrix-controlled release for more 6-8 h. The release data depends on drug loading and polymer structure. The possibility of application of polyvinyl alcohol for prolongation of anesthetics is show.
References
1. Li Wan Po A., Mhando J.R. Formulation of sustained-release products: dissolution and diffusion-controlled release from gelatin films // Int. Journ. Pharm. – 1984. –Vol. 20.– P.87-98
2. Ishuda V., Nambu N., Nagai T. Mucosal dosage form of lidocaine for toothache using hydroxypropyl cellulose and carbopol // Chem. And Pharm. Bull. – 1982. – № 3. –P.980-984.
2. Ishuda V., Nambu N., Nagai T. Mucosal dosage form of lidocaine for toothache using hydroxypropyl cellulose and carbopol // Chem. And Pharm. Bull. – 1982. – № 3. –P.980-984.
Batyrbekov E.O., Borisova A.E. DEVELOPMENT OF POLYMERIC DOSAGE FORMS FOR SUSTAINED RELEASE LOCAL ANESTHETICS. International Journal Of Applied And Fundamental Research. – 2018. – № 6 –
URL: www.science-sd.com/478-25467 (11.02.2026).











 PDF
PDF